TH4001
Design and Construction of the BPL-RFQ
D.-M. KONG, Z.-H. LUO, J.-M. QIAO, S.-H. WANG, W.-W. XU,
IHEP-Beijing
BPL-RFQ is a four-rod type linac structure, currently under construction,
that will operate at a radio frequency of 201.25 MHz. According to the
design, it can accelerate protons from 40 keV to 750 keV with a pulse beam
current of 60 mA. BPL-RFQ is planned as the Beijing Proton Linac's injector
instead of the present bulky Cockroft-Walton accelerator. This paper
describes the general layout, design features, field distribution
measurements, and recent status of the BPL-RFQ. The field distribution
measurements have been done for the model. In the case of unmodulating
electrodes, the results were: the field distribution asymmetry is near 2.5%
in the azimuthal direction and the field flatness is near 3.5% in the
longitudinal direction. The formal electrode modules and the cavity is being
assembled and tested, and the BPL-RFQ rf power supply is completed. An rf
power of 400 kW has been obtained on the test load. The ion source has been
tested and a beam current of 150 mA has been reached under 40 kV. The control
subsystem, emittance measurement devices, and solenoids have also been tested.
Commissioning of the BPL-RFQ will start in the near future.
Classification Category: A02
TH4002
Testing of a New 2 MeV RFQ and Perspective of 433 MHz
Linac for Applied Purposes*
Y. V. AFANASIEV, Y. N. GAVRISH, A. K. LIVEROVSKY, V. G. MUDROLUBOV, A. P.
STROKACH, Y. A. SVISTUNOV, M. F. VOROGUSHIN, EIEA
A new 2-MeV, 433-MHz RFQ has been built and tested with a proton beam up to
15 mA. It has been fabricated from AMG-6 aluminum alloy and installed,
replacing the previous 1.8 MeV RFQ. The results of frequency adjustments and
field alignment are presented. There are significant improvements in field
distribution and beam emittance of the output injector in comparison with the
1.8-MeV accelerator data. Simultaneously work on the alternate phase focusing
(APF) structure with 2-MeV input energy and 11-MeV output energy continued.
Theoretical and experimental research connected with different applications of
2-MeV linac or 11-MeV tandem RFQ and APF linacs were carried out at NPK LUTS
of the Efremov Institute last year. Methods and devices of elemental analysis
and contraband detection system for the 2-MeV linac and use of the 11-MeV
tandem for PET-system or as part of a big linac are discussed briefly.
*Work supported by Minatom of Russia.
Classification Category: A02
TH4003
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4004
High Power Conditioning of the 202 MHz IH Tank 2 at
the CERN Linac3
J. BROERE, H. KUGLER, M. VRETENAR, CERN; U. RATZINGER, GSI Darmstadt;
B.
KRIETENSTEIN, TU-Darmstadt
High accelerating gradients are very attractive for future machines, and,
in particular, for high current heavy ion linac projects like the "Inertial
Fusion Driver". In order to explore the maximum field achievable in an
Interdigital-H type structure, an experiment has been carried out at CERN on
the Lead Ion Linac (Linac3). After the 1997 run, the RF amplifiers were
rearranged in order to allow the feeding of the IH Tank number 2 (1.55 m long,
28 gaps, frequency of 202.56 MHz) with up to 2 MW pulsed RF power. After two
weeks of conditioning at pulse lengths variable between 200 microseconds and 1
millisecond with a constant pulse repetition rate of 0.8 Hz, the maximum
effective acceleration gradient achieved was 10.5 MV/m. This corresponds to a
local field maximum of 5 times the Kilpatrick limit, and to fields in excess
of 3.5 times Kilpatrick on large portions of the drift tube surfaces. This
paper reports the conditioning procedure applied, the measurements of field
emission current at different voltages and pulse lengths, the determination of
the surface field enhancement factor as well as the calculation of the
electric field distribution for the gap with the highest surface fields.
Classification Category: A02
TH4005
Design of the KOMAC H+/H- RFQ Linac
J.M. HAN, Y.S. CHO, B.H. CHOI, KAERI; S.H. JIN, I.S. KO, PAL-POSTECH;
B.S.
KANG, B.S. HAN, SHIC
A 350 MHz, cw Radio-Frequency Quadrupole (RFQ) will be built to produce 20
mA of H+/H- beam at 3 MeV for the Korea Multipurpose
Accelerator Complex (KOMAC) projects 1GeV linac. The beam dynamics and the
engineering design of the Low Energy Beam Transport (LEBT) and RFQ are
described. The detail design of a vacuum pumping system for the KOMAC RFQ is
presented.
Classification Category: A02
TH4006
RFQ-Accelerators for Radioactive Ion-Beams
T. SIEBER, O. KESTER, D. HABS, LMU Muenchen; A. SCHEMPP, IAP-Univ. of
Frankfurt
For the REX-ISOLDE LINAC at CERN a 4-rod-RFQ is built up and tested at
Munich. This RFQ has a length of 3 m and will accelerate neutron-rich ions
from 5 keV/u to 300 keV/u. It operates at a resonant-frequency of 101.28 MHz
with a duty-cycle of 10%. The transmission has been calculated with PARMTEQ to
98%. In the poster the mechanical characteristics of the RFQ and the results
of the rf-measurements will be presented.
Furthermore we want to show, that - alternative to the well tested and
reliable 4-rod-RFQ-structures - IH-type RFQ's like the new GSI
high-current-injector-RFQ [1] (resonant-frequency: 36 MHz) could also operate
at frequencies around 100 MHz. For the planned fission fragment accelerator of
the Munich high-flux reactor, investigations are under progress on such an
IH-RFQ. Advantages of this structure might be a high efficiency, indirect
electrode-cooling and the possibility to use finger drift-tubes in addition.
The IH-RFQ will operate at 101 MHz and accelerate ions with A/q=6.3 to
about 300 keV/u. The particle dynamics will be similar to the REX-RFQ.
MAFIA-calculations for a 0.75 m model and for the 3 m power-resonator will be
presented together with first measurements on the model.
[1] U. Ratzinger, Proc. of LINAC '96, CERN, Geneva.
Classification Category: A02
TH4007
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4008
Recent Developments of the Folded-Coaxial RFQ for the RIKEN Heavy Ion
Linac
O. KAMIGAITO, A. GOTO, Y. MIYAZAWA, T. CHIBA, M. HEMMI, M. KASE, S.
KOHARA,
E. IKEZAWA, T. NAKAGAWA, Y. YANO, RIKEN
In August 1996, a new injector system for the RIKEN heavy ion linac (RILAC)
was installed, which consists of an 18-GHz ECR ion source and a
variable-frequency RFQ based on a folded-coaxial resonator. The beam
intensities have remarkably increased after the installation. For example, the
intensity of Xe beam has increased by about two orders of magnitude compared
with those using the Cockcroft-Walton injector. The maximum power of the beam
extracted from the RILAC and that from the ring cyclotron have reached 560 W
and 2 kW, respectively. In order to achieve these results, the maximum
extraction voltage of the ECR ion source was raised from 10 kV to 20 kV in
August 1997. The RFQ vanes were replaced correspondingly at the same time.
Another important result we have obtained is that the transmission efficiency
of the RILAC has exceeded 80 % by use of the pre-buncher placed before the
RFQ. Operational experiences of the RFQ as well as recent developments are
described in this paper.
Classification Category: A02
TH4009
First Beam Test with the ISAC RFQ
R.E. LAXDAL, R. BAARTMAN, G. DUTTO, K. FONG, K. JAYAMANNA, M.
MACDONALD, A.
MITRA, R. POIRIER, W. RAWNSLEY, L. ROOT, B. UZAT, J. WELZ, TRIUMF
The ISAC RFQ is a 35 MHz, split-ring, four vane structure designed to
accelerate ions of A/q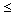 30 from 2keV/u to 150keV/u in cw
mode. When
completed the RFQ will comprise 19 modules, each composed of one split-ring
connected to 40cm of electrodes in quadrature for a total length of about 8m.
The first 7-ring portion of the RFQ is scheduled for testing with beam in an
interim configuration in early summer of this year. A copper wall internal to
the RFQ tank isolates the rf power to the electrode region. Electrostatic
quadrupoles are installed in the remainder of the tank to transport the beam
to a downstream diagnostic station. An injector composed of a 2.45GHz ion
source in a CUSP geometry and an electrostatic LEBT and matching section
delivers stable light ions to the RFQ. The beam is pre-bunched with an 11.7MHz
pseudo saw-tooth waveform across a single gap to satisfy an experimental
requirement for 90ns between beam bursts. The diagnostic station consists of
Faraday cups, a fast Faraday cup, an emittance rig, and an analyzing magnet.
The complete test set-up will be described and the results of commissioning
the injector and testing the RFQ will be summarized.
30 from 2keV/u to 150keV/u in cw
mode. When
completed the RFQ will comprise 19 modules, each composed of one split-ring
connected to 40cm of electrodes in quadrature for a total length of about 8m.
The first 7-ring portion of the RFQ is scheduled for testing with beam in an
interim configuration in early summer of this year. A copper wall internal to
the RFQ tank isolates the rf power to the electrode region. Electrostatic
quadrupoles are installed in the remainder of the tank to transport the beam
to a downstream diagnostic station. An injector composed of a 2.45GHz ion
source in a CUSP geometry and an electrostatic LEBT and matching section
delivers stable light ions to the RFQ. The beam is pre-bunched with an 11.7MHz
pseudo saw-tooth waveform across a single gap to satisfy an experimental
requirement for 90ns between beam bursts. The diagnostic station consists of
Faraday cups, a fast Faraday cup, an emittance rig, and an analyzing magnet.
The complete test set-up will be described and the results of commissioning
the injector and testing the RFQ will be summarized.
Classification Category: A02
TH4010 (oral
poster TH3001)
Status of the ISAC Accelerator for Radioactive
Beams
R.E. LAXDAL, R. BAARTMAN, P. BRICAULT, G. DUTTO, R. POIRIER, P.
SCHMOR,
TRIUMF
The ISAC radioactive beam facility under construction at TRIUMF includes a
500MeV proton beam (I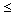 100microA) impinging on a thick
target, an on-line
source, a mass-separator, an accelerator complex, and experimental areas. The
accelerator chain includes a 35MHz RF Quadrupole (RFQ) to accelerate beams of
A/q
100microA) impinging on a thick
target, an on-line
source, a mass-separator, an accelerator complex, and experimental areas. The
accelerator chain includes a 35MHz RF Quadrupole (RFQ) to accelerate beams of
A/q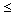 30 from 2keV/u to 150keV/u and a post-stripper,
105MHz variable energy
drift tube linac (DTL) to accelerate ions of 3
30 from 2keV/u to 150keV/u and a post-stripper,
105MHz variable energy
drift tube linac (DTL) to accelerate ions of 3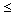 A/q
A/q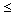 6 to a final energy
from 0.15 to 1.5MeV/u. The accelerators have several noteworthy features. Both
linacs are required to operate cw to preserve beam intensity. The RFQ, a four
vane split-ring structure, has no bunching section; instead the beam is
pre-bunched at 11.7MHz with a single-gap, pseudo saw-tooth buncher. The
variable energy DTL is based on a unique separated function approach with five
independent interdigital H-mode (IH) structures providing the accleration and
quadrupole triplets and three-gap bunching cavities between tanks providing
transverse and longitduinal focussing respectively. The present status of the
accelerator complex will be reported. In particular, first beam tests with the
RFQ and power tests of both the first DTL IH tank and DTL buncher are
scheduled for this summer.
6 to a final energy
from 0.15 to 1.5MeV/u. The accelerators have several noteworthy features. Both
linacs are required to operate cw to preserve beam intensity. The RFQ, a four
vane split-ring structure, has no bunching section; instead the beam is
pre-bunched at 11.7MHz with a single-gap, pseudo saw-tooth buncher. The
variable energy DTL is based on a unique separated function approach with five
independent interdigital H-mode (IH) structures providing the accleration and
quadrupole triplets and three-gap bunching cavities between tanks providing
transverse and longitduinal focussing respectively. The present status of the
accelerator complex will be reported. In particular, first beam tests with the
RFQ and power tests of both the first DTL IH tank and DTL buncher are
scheduled for this summer.
Classification Category: A02
TH4011
Operation of the VE-RFQ Injector for the ISL Cyclotron*
O. ENGELS, A. SCHEMPP, F. HÖLLERING, IAP-Univ. of Frankfurt; J.
HÄUSER, NTG, Neue Technologien; H. HOMEYER,
W. PELZER, A. DENKERT, Hahn-Meitner-Institut
The VE-RFQ-injector for the cyclotron at HMI in Berlin is now in operation.
The ECR-source together with the RFQs supply heavy ion beams with 90 - 360
keV/u for q/A > 0.15, matched to the isochronous cyclotron. Properties of
the new injector and results of rf-measurements, high power tests and beam
measurements are presented.
*Work supported by the BMBF.
Classification Category: A02
TH4012
Design of a High Current RFQ Injector with High Duty Factor*
H. VORMANN, A. SCHEMPP, U. BESSLER, IAP-Univ. of Frankfurt; C. W.
PLANNER, A. LETCHFORD, RAL
An RFQ injector with a duty factor up to 10% is planned for the spallation
source ISIS at Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (RAL). The accelerator will be a
Four Rod RFQ with directly cooled electrodes, operating at 202 MHz. The RFQ
will provide a H- beam current up to 50 mA with an output energy of
665 keV (input energy 50 keV). The beam dynamics, rf and mechanical designs
are presented.
* Work supported by the BMBF.
Classification Category: A02
TH4013
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4014
Proposal to use PIVAIR as a 30 GHz High-Power Generator
J. L. RULLIER, J. GARDELLE, T. LEFEVRE, CEA/Cesta; J.T. DONOHUE,
CENBG
The Two-Beam Accelerator (TBA) is under active study both at Lawrence
Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) and at CERN. In the TBA an extremely
intense low-energy electron beam is bunched at the desired operating
frequency, and upon passing through resonant cavities generates high-gradient
radio-frequency (RF) power for accelerating the main beam. Among the
different approaches to the production of a suitable drive-beam, the use of a
free-electron laser has been proposed. Recently at CEA-CESTA, encouraging
results in this direction have been obtained. To extend this work, we propose
the use of the induction accelerator "PIVAIR" at CESTA (7 MV, 4 kA) as a test
stand for high power RF structure experiments at 30 GHz. Our research program
for PIVAIR includes:
- Production of a drive beam current profile designed to compensate beam
loading,
- High power tests of a CLIC Transfer Structure,
- Tests of the 30 GHz RK-CLIC components.
Classification Category: A04
TH4015
First Order Design Study of an Accelerator Beamline
for the PEARL FEL
M. C. LAMPEL, G. H. Gillespie Associates, Inc.; J. M. J. MADEY, Duke
University; R. J. BURKE, Arcata Systems
The Pan-Oceanic Environmental and Atmospheric Research Laboratory (PEARL)
consortium has proposed the deployment of a ship-based FEL facility for
advanced atmospheric and environmental research and to develop remote sensor
technology. The FEL is intended to have an optical output from approximately
20 microns down to 1/3 micron, with up to 1 kW average power at longer
wavelengths. The accelerator will operate over a wide range of beam currents
and energies to meet these goals. The proposed shipboard FEL must meet design
constraints in compactness and efficiency. The accelerator beamline, upstream
of the FEL resonator, includes a 4.5 MeV rf gun, pulse length compression
chicane, and four 1.26 meter long travelling wave (TW) accelerator sections.
First order focussing along the beamline is provided by quadrupole magnets.
First order beam dynamics for this beamline are studied using TRACE 3-D with a
self-consistent TW accelerator model incorporated into it. Parametric studies
of beamloading effects on accelerator efficiency and beam transport are
performed. Beamline layouts, taking into account the physical dimensions and
operating parameters of the equipment will be studied to determine the
baseline beamline design for further, higher order simulations, on the way
towards an optimized design.
Classification Category: A04
TH4016
First Lasing of the JAERI FEL Driven by the Superconducting RF
Linac
E.J. MINEHARA, M. SUGIMOTO, M. SAWAMURA, R. NAGAI, N. KIKUZAWA, N.
NISHIMORI, JAERI
First and stable laser oscillation has been obtained at a wavelength of 24
micrometer using the JAERI (Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, Tokai)
superconducting rf linac based FEL driver. Electron beam energy and
resolution are 15.8MeV, and 0.6% respectively, the beam current and pulse
width a few mA and 0.8ms or less, respectively. The optical resonator with a
52 period hybrid planer undulator (K=0.7) is 1.7m long and uses Au coated Cu
mirrors of 120mm diameter. The optical axes and distance of the mirrors is
adjusted by remotely controlled actuators in order to coincide with the
electron beam and micro pulse repetition rate, respectively, before the
oscillation. The power is scattered at least around 8 orders of the magnitude
higher than that of the spontaneous emission. During the first successfull
operation, the highest FEL power was measured to be several tens watts in
average. The FWHM of the FEL spectrum is less than 0.6 micrometer, which
corresponds to 2.5% of the wavelength. The tuning range of the cavity is about
15 micrometer.
Classification Category: A04
TH4017
Recent Performance of the JAERI Superconducting Linac for
FEL
M. SAWAMURA, R. NAGAI, N. KIKUZAWA, N. NISHIMORI, E.J. MINEHARA,
JAERI
Far-infrared FEL oscillation using the superconducting linac has succeeded
in JAERI. The linac consists of a 250kV electron gun, a subharmonic
normal-conducting buncher (SHB) of 83.3MHz, two single-cell and two 5-cell
superconducting cavities of 499.8MHz. The gun was typically operated around
200 kV to reduce space charge effects. The combination of the SHB and two
single-cell cavities enabled high current beam of more than ten amperes by
utilizing a thermionic cathode and a grid pulsing. The two single-cell
cavities were powerful enough to compress high current beam and to reduce the
space charge effects. Calculations utilizing the modified PARMELA code showed
that the electron bunch of 3 ns from the electron gun was finally compressed
to be 20-35 ps with the energy resolution of 2.3-3.1 % in FWHM after the two
single-cell cavities. The major part of the transverse emittance hardly
increased. FWHM bunch length and energy resolution were measured to be 22ps
and 3% or less, respectively. The measured results agreed with the
calculated. This showed the validity of the linac design for the FEL.
Classification Category: A04
TH4018
Electron Beam Charge State Amplifier (EBQA): Concept
and Simulations*
J. C. DOOLING, J. A. NOLEN, ANL
A concept referred to as an EBQA is presented for stripping low energy
radioactive ions from 1+ to higher charge states. In an EBQA, continuous
beams of 1+ radioactive ions extracted from standard Isotope-Separator-Online
(ISOL) sources are passed through a high-density electron beam which is confined
by a solenoidal magnetic field in a geometry similar to an Electron Beam Ion
Source. An EBQA is potentially useful to increase the charge states of ions
prior to post acceleration at ISOL radioactive beam facilities. The efficiency
of stripping ions from q=1+ to 2+ is evaluated as a function of electron beam
radius at constant current with solenoid field, injected ion energy, and ion
beam emittance used as parameters. With a 5 keV, 1 A electron beam, stripping
efficiencies of 38% are calculated for 0.1 keV, mass 132 ions with a
single pass through an 8 Tesla by 1 m long solenoid. Multi-pass
configurations to achieve 3+ or 4+ charge states are also conceivable. The
calculated efficiencies depend inversely on the initial ion beam emittances.
Hence, the use of a helium-buffer-gas, ion-guide stage to improve the
brightness of the 1+ beams would enhance the performance of the EBQA.
Examples of how an EBQA could be used at the front end of a continuous-wave
radioactive beam post accelerator will also be presented.
*This work is supported by the U. S. Department of Energy under contract
W-31-109-ENG-38.
Classification Category: A06
TH4019
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4020
Long Range Plan Proposal for an Extension to ISAC
R. BAARTMAN, R. LAXDAL, L. ROOT, TRIUMF
A radioactive ion beam facility, ISAC, is presently under construction at
TRIUMF. The post-accelerator comprises a 35 MHz RFQ to accelerate ions of A/q
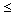 30 from 2 keV/u to 150 keV/u and a post-stripper room
temperature 105
MHz DTL to accelerate ions of 3
30 from 2 keV/u to 150 keV/u and a post-stripper room
temperature 105
MHz DTL to accelerate ions of 3 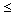 A/q
A/q 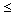 6 to a final energy fully
variable up to 1.5 MeV/u. Both linacs are required to operate in cw mode. For
the next five year plan, it is intended to increase the final energy above the
Coulomb barrier (roughly 6.5 MeV/u) and broaden the mass range up to roughly A
= 150. The ISAC-2 proposal will utilize the existing RFQ. Masses higher than
30 will require ECR ion sources and/or charge boosters. To optimize the total
accelerating voltage while utilizing a single stripping stage requires that
the stripping energy be increased from 150 keV/u to 400 keV/u. A 105 MHz room
temperature IH-DTL would supply the required 7.5 MV from RFQ to stripper. The
post-stripper linac is required to accelerate ions of A/q
6 to a final energy fully
variable up to 1.5 MeV/u. Both linacs are required to operate in cw mode. For
the next five year plan, it is intended to increase the final energy above the
Coulomb barrier (roughly 6.5 MeV/u) and broaden the mass range up to roughly A
= 150. The ISAC-2 proposal will utilize the existing RFQ. Masses higher than
30 will require ECR ion sources and/or charge boosters. To optimize the total
accelerating voltage while utilizing a single stripping stage requires that
the stripping energy be increased from 150 keV/u to 400 keV/u. A 105 MHz room
temperature IH-DTL would supply the required 7.5 MV from RFQ to stripper. The
post-stripper linac is required to accelerate ions of A/q 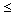 7 from 0.4 to
6.5 MeV/u (42.7 MV). Both a room temperature and a superconducting DTL
structure have been considered. The room temperature approach would consist of
long IH tanks (GSI model). The superconducting structure would consist of
short (2 to 4 cell) independently-phased cavities (ATLAS model). In this paper
we compare the various ISAC-2 options and present first order linac designs,
cost estimates and staging scenarios.
7 from 0.4 to
6.5 MeV/u (42.7 MV). Both a room temperature and a superconducting DTL
structure have been considered. The room temperature approach would consist of
long IH tanks (GSI model). The superconducting structure would consist of
short (2 to 4 cell) independently-phased cavities (ATLAS model). In this paper
we compare the various ISAC-2 options and present first order linac designs,
cost estimates and staging scenarios.
Classification Category: A06
TH4021
Status of the REX-ISOLDE LINAC*
O. KESTER, D. HABS, T. SIEBER, R. RAO, K. RUDOLPH, A. KOLBE, P.
THIROLF,
LMU München; R. VON HAHN, H. PODLECH, R. REPNOW, D. SCHWALM, MPI für
Kernphysik; A. SCHEMPP, K.-U. KÜHNEL, C. WELSCH, IAP-Univ. of Frankfurt; U.
RATSINGER, GSI Darmstadt; and the REX-ISOLDE collaboration
The Radioactive beam Experiment (REX-ISOLDE) [1] a pilot experiment testing
a new concept of post acceleration of radioactive ions at ISOLDE/CERN is under
progress. Radioactive singly charged ions delivered by the on-line mass
separator ISOLDE are accumulated in a Penning trap, then charge breeded to A/q
< 4.5 in an electron beam ion source (EBIS) and finally accelerated in a
LINAC from 5 keV/u to the final energy between 0.8 and 2.2 MeV/u. The resonant
structures of the LINAC consist of a Radio Frequency Quadrupole (RFQ)
accelerator, an interdigital H-type structure (IH) and three seven gap
resonators, which allow a variation of the final beam energy. New beam line
calculations of the mass separator and the matching section between RFQ and
IH-structure have been carried out. First low level measurements have been
done and power tests of the RFQ will be performed at the Munich Tandem
Laboratory in the middle of 1998. A test beam line including a duoplasmatron
ion source, an electrostatic quadrupole lens system and a diagnostic box is
being built up. The vacuum tank of the IH-structure is in production and will
be copper plated in June and July. First low level measurements in comparison
with model measurements [2] and MAFIA calculations will be presented. The
production of the resonant structures and of the first tanks of the seven gap
resonators is almost completed. First low level and power measurements are
foreseen in the middle of the year and will be shown.
*Work supported by BMBF FKZ 06 LM 868 I (2).
[1] D. Habs et al., CERN-ISC94-25.
[2] B. Keil, Diploma thesis, University of Munich, August 1997.
Classification Category: A06
TH4022
Relativistic-Klystron Two-Beam Accelerator as a Power Source for
Future Linear Colliders*
G. A. WESTENSKOW, T. L. HOUCK, LLNL; D. E. ANDERSON, S. EYLON, E.
HENESTROZA, S.M. LIDIA, D. L. VANECEK, S. S. YU, LBNL
The technical challenge for making two-beam accelerators into realizable
power sources for high-energy colliders lies in the creation of the drive beam
and in its propagation over long distances through multiple extraction
sections. This year we have been constructing a 1.2-kA, 1-MeV, induction gun
for a prototype relativistic klystron two-beam accelerator (RK-TBA). The
electron source will be a 3.5"-diameter, thermionic, flat-surface cathode with
a maximum shroud field stress of approximately 165 kV/cm. Additional design
parameters for the injector include a pulse length of over 150-ns flat top (1%
energy variation), and a normalized edge emittance of less than 200 pi-mm-mr.
The prototype accelerator will be used to study physics, engineering, and
costing issues involved in the application of the RK-TBA concept to linear
colliders. We have also been studying optimization parameters, such as
frequency, for the application of the RK-TBA concept to multi-TeV linear
colliders. As an rf power source the RK-TBA scales favorably up to frequencies
around 35 GHz. An overview of this work with details of the design and
performance of the prototype injector, beam line, and diagnostics will be
presented.
*The work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy
by LLNL under contract W-7405-ENG-48, and by LBNL under contract
AC03-76SF00098.
Classification Category: A07
TH4023
Achromat with Linear Space Charge for Bunched Beams*
D. RAPARIA, J. G. ALESSI, Y. Y. LEE, W. T. WENG, BNL
The standard definition for an achromat is a transport line having zero
values for the spatial disperson (R16) and the angular dispersion (R26). In
presence of linear space charge this definition of achromaticity does not
hold. The linear space charge provides coupling between (a) bunch spatial
width and bunch length (R15) and (b) bunch angular width and bunch length
(R25). Therefore, achromaticity should be redefined as a line having zero
values of the spatial disperson (R16), the angular dispersion (R26), and matix
elements R15 & R25. These additional conditions (R15=R25=0) can be
achieved, for example, with two small RF cavities, to cancel space charge
effects. An example of the application of this technique to the Spallation
Neutron Source (SNS) high energy beam transport line will be presented.
* Work performed under the auspices of the U. S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: D01
TH4024
A Possible Particle-Core Approach to Mismatched Beams in a Periodic
Focusing Channel
M. IKEGAMI, M. MIZUMOTO, JAERI
A method is derived for applying the particle-core analysis to mismatched
beams in a periodic focusing channel in cases where the core oscillation is
stable. By carefully choosing the parameters to yield a favorable core
frequency, a Poincare surface of section plot is obtained. The plots for a
periodic solenoid channel exhibit a striking resemblance with the continuous
focusing case, while those for a FODO channel exhibit a strong chaosity which
is not seen in the corresponding continuous focusing situation. It suggests
that the strong modulation of the core oscillation due to an
alternating-gradient focusing field affects test particle stability. Some
typical numerical results and a way to find adequate parameters are
presented.
Classification Category: D01
TH4025
Halo Formation by Mismatch for High Intensity Bunched
Beams
M. PABST, K. BONGARDT, FZJ; A. LETCHFORD, RAL
In high intensity proton linacs even small particle loss causes activation
of the accelerator components. Minimizing the losses is therefore a major task
of the beam dynamical design. Losses are strongly correlated to the formation
of a halo around the beam core. The formation of the halo is caused by
nonlinear space charge forces, particle resonances and is enhanced by
mismatch. For a bunched beam the oscillation of the three envelopes due to
mismatch can be described by three eigenfrequencies. The corresponding modes
differ in their radial and axial amplitudes. In this contribution the
influence of different mismatches on the phase space distribution of bunched
beams is studied in detail by Monte-Carlo simulations. Examples are given for
varying the tune depressions and equipartitioning ratios.
Classification Category: D01
TH4026
Self-consistent 3D Simulations of Longitudinal Halo in
RF-linacs
J. J. BARNARD, S. M. LUND, LLNL; R. D. RYNE, LANL
In order to prevent activation of the beam pipe walls and components of a
high power ion accelerator, beam loss must be minimized. Here we present
self-consistent, 3D particle-in-cell simulations of longitudinally mismatched
beams, including the effects of rf non-linearities, using parameters based on
the Accelerator Production of Tritium linac design. In particular, we
explore the evolution of the longitudinal halo distribution, i.e. the
distribution of particles in longitudinal phase space with oscillation
amplitudes significantly larger than amplitudes of particles in the main body
or "core" of the beam. When a particle reaches a sufficiently large amplitude
longitudinally, it can be lost from from the rf bucket, and consequently loses
synchronisim with the rf wave. Such particles will lose energy and so be
poorly matched to the transverse focusing field and consequently can be lost
transversely. We compare the present simulations, in which all particles
contribute self-consistently to the self field, to predictions of a core/test
particle model, in which the core distribution has uniformly distributed
charge and does not evolve self-consistently. Effects of self consistent,
non-linear space charge forces, non-linear rf focusing and transverse
longitudinal coupling on envelope mismatch induced beam halo are explored
through comparisons of both models.
Classification Category: D01
TH4027
Analytic Model of Ion Emission from the Focus of an Intense
Relativistic Electron Beam on a Target*
G. J. CAPORASO, LLNL
Advanced radiographic systems for stockpile stewardship require very small
x-ray sources to achieve the required resolution. Focusing multi-kiloampere
beams to diameters on the order of 1 mm onto a Bremsstrahlung target leads to
the generation of axial electric fields on the order of several MV/cm which
act to extract ions out of the surface plamsa and accelerate them upstream
into the beam. These backstreaming ions act as a distributed electrostatic
lens which can perturb the focus of the electron beam in a time varying manner
during the pulse. An analytic model of the diode extraction is presented for
a particular target geometry along with scaling laws for the perturbation of
the focal spot.
*This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of
Energy by the LLNL under Contract
No.W-7405-Eng-48.
Classification Category: D01
TH4028
Trapping Backstreaming Ions from an X-ray Converter using an Inductive
Cell*
B.R. POOLE, Y.-J. CHEN, T.L. HOUCK, LLNL
High current electron beams have been used as x-ray drivers for the x-ray
radiography. Typically, several thousand amperes of electron beam current at
20 MeV is focused to a millimeter spot size on a x-ray converter. Within a
single pulse, the heating of the target by the electron beam will lead to
rapid desorption of surface contaminants. The space charge potential of the
electron beam will pull ions out of this plasma layer upstream into the beam.
These backstreaming ions can act as a focusing lens which cause the beam to be
overfocused at a waist upstream. The final beam spot size on the target would
then be larger than intended, and the x-ray radiography resolution is reduced.
We have designed a self-biased ion trap for the Experimental Test Accelerator
(ETA-II) beam by using an Advanced Test Accelerator (ATA) inductive cell to
prevent the backstreaming ions from moving upstream and forming a long ion
focusing channel. We have studied the effects of this type of ion trap on the
final focusing of the electron beam with the ETA-II beam parameters and the
proposed Advanced Hydro Facility (AHF) beam parameters. Simulation results
will be presented.
*This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of
Energy by the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under contract No.
W-7405-Eng-48
Classification Category: D01
TH4029
Analysis of the Frequency Dependence of the
Longitudinal Coupling Impedance of a Small Hole in a Coaxial
Liner
A.V. FEDOTOV, R.L. GLUCKSTERN, Univ. of Maryland
We recently developed a general analysis for a rectangular slot in the
inner conductor of a coaxial liner, which allowed us to investigate the
coupling impedance numerically. In the present paper we obtain analytic
expressions for a small hole of arbitrary shape which includes effects of
energy propagation along the inner beam pipe and/or outer coaxial pipe. This
allow us to understand the structure of the impedance in the frequency region
near the cutoffs of the beam pipe. We then extend our analysis to a hole in a
wall of finite thickness.
Classification Category: D01
TH4030
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4031
Beam Dynamics Simulations of the LANSCE
Linac
F. MERRILL, L. RYBARCYK, LANL
Detailed beam dynamics calculations of the LANSCE Linac have been performed
using multi-particle simulation codes. The LANSCE accelerator produces both
H+ and H- beam and is comprised of Cockcroft-Walton
injectors, a 100MeV drift-tube linac and an 800MeV side-coupled linac.
Several improvements to the simulations of H+ and H-
beams have recently been made. These include the use of more accurate input
distributions and a better estimate of beam neutralization in the low energy
beam transport. Better estimates of the accelerating fields in the drift-tube
linac have also been determined through measurements and modeling. With these
improvements better agreement has been achieved between the predictions and
measurements of RMS beam parameters and beam losses for both beams. The
details of the simulations along with predictions are presented in comparison
with measurements for both H+ and H- beams.
Classification Category: D02
TH4032 (oral
poster TH3002)
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4033
The Nonlinear Transverse RF Field Effects on the Beam
Dynamics*
X. SUN, Y. LIN, Tsinghua University
The nonlinear transverse RF field effects on the low energy and emittance
dominated electron beams are investigated theoretically. Without any external
magnetic focusing devices and in pursuit of high shunt impedance, the
nonlinear transverse RF field effects should not be neglected. The evolution
of the electron beam phase space distribution is studied by taking into
account the nonlinear transverse RF fields. As a result of the nonlinear
transverse RF field effects, the emittance growth occurs mainly in the first
cavity and is associated with the initial phases of the beam, the injection
voltages of the electron gun and the accelerating gradients in the first
cavity.
*Work supported by the National Science Foundation of China.
Classification Category: D02
TH4034 (oral
poster TH3003)
The SCHERM Space Charge Routine --- Limitations and
Solutions
P. LAPOSTOLLE*, S. VALERO, N. PICHOFF, J.-M. LAGNIEL, S. NATH**,
CEA/DSM/DAPNIA/SEA
The SCHERM space charge routine, reported in the 1996 linac conference, is
based on representing the charge density distribution in a bunch with an
Hermite series expansion. In spite of its initial promise, rigorous analyses
have revealed problems which are purely of mathematical origin. Mathematical
solutions of the difficulties are being tested in a continuous confined (no
acceleration), as well as a periodic accelerating (6.7 MeV to 100 MeV) channel
with highly tune-depressed beams. Here, we discuss the problems with series
representation, solutions around it and results of the modified method applied
to cases stated above.
* Consultant, SEA/CEA, Saclay
** On sabbatical from LANL, Los Alamos, NM, USA
Classification Category: D04
TH4035
A Multi-Platform Graphic User Interface for the
Particle Optics Code MARYLIE
G. H. GILLESPIE, B. W. HILL, M. C. LAMPEL, H. MARTONO, J. M. MOORE, K.
J.
RYAN, G.H. Gillespie Associates, Inc.; A. J. DRAGT, Univ. of Maryland
An advanced graphic user interface (GUI) is being developed for use with
the particle optics program MARYLIE. MARYLIE is based on a Lie algebraic
formulation of charged particle trajectory calculations and is particularly
useful for particle tracking and the analysis of linear and nonlinear lattice
properties. The GUI for MARYLIE uses the Multi-Platform Shell for Particle
Accelerator Related Codes, a software framework developed specifically to
support accelerator modeling and simulation. Transport element icons are
selected from a palette and assembled into beamlines by graphical
construction. Optical cells and lattices composed of element groups may be
defined as sublines, and any element or subline can be replicated using an
alias element. The icon-based beamlines generate entries for the #beam, #menu
and #lines components of the MARYLIE Master Input File (MIF). Frequent
computations, such as creating maps or generating particle distributions, are
encapsulated into interactive GUI commands which create corresponding entries
in the #menu, #lines and #labor components of the MIF. An icon-based
description of procedural processes is being developed to support more complex
MARYLIE analysis tasks that utilize the #lumps and #loops components.
Progress on the development of this GUI for MARYLIE will be described, and the
software will be demonstrated.
Classification Category: D04
TH4036
X-band Klystron Output Cavity Simulation
H. TSUTSUI, S. MATSUMOTO, S. MICHIZONO, Y.H. CHIN, S. FUKUDA, KEK
Design of X-band (11.424GHz) klystrons capable of 120MW (XB72K series) is
undergoing at KEK. MAGIC2D, a 2.5 dimensional particle-in-cell code, was
introduced in KEK last year for the design of the next klystron XB72K-10 with
a 4-cell travelling wave type output cavity. Since the coupler of the output
cavity is not axisymmetrical, the structure cannot be simulated directly by 2
dimensional codes. To make 2 dimensional simulation possible, the notion of
S-matrix is introduced, and is calculated using the eigenvalue solver of MAFIA
codes. The saturated output powers calculated by MAGIC2D agree well with the
measurements of KEK XB72K-8 and SLAC XL-4 klystrons. The design of XB72K-10 is
also presented.
Classification Category: D04
TH4037
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4038
Designing Double-Gap Linear Accelerators for a Wide Mass
Range
W. LYSENKO, LANL
For applications like ion implantation, rf linacs using double-gap
structures with external resonators can be used because they are practical at
low frequencies. However, since the two gaps associated with a given
resonator cannot be individually phased, it is not obvious how to design a
linac that can efficiently accelerate particles having different mass/charge
ratios. This paper describes the beam dynamics of double-gap rf linacs. We
show how to maximize the range of mass/charge ratios that a linac design can
handle, subject to the constraint that the gap voltage not exceed a given
value. The range of mass/charge ratios that can be accelerated depends on the
choice of synchronous phases on the two gaps. Our theory tell us how to
rescale a linac tune (i.e., reset the voltages and phases) so that a new
particle, having a different mass or charge, will behave similarly to the
original particle.
Classification Category: D02
TH4039
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4040
Physics Design of the DARHT 2nd Axis Accelerator Cell*
T.L. HOUCK, Y.-J. CHEN, C. SHANG, LLNL; L.L. REGINATO, S.S. YU, LBNL;
R.
BRIGGS, SAIC; D. BIRX, Science Research Laboratory
The next generation of radiographic machines based on induction
accelerators require very high brightness electron beams to realize the
desired x-ray spot size and intensity. This high brightness must be maintained
throughout the beam transport, from source to x-ray converter target. The
accelerator for the second-axis of the Dual Axis Radiographic Hydrodynamic
Test (DARHT) facility is being designed to accelerate a 4-kA, 2-5s pulse of
electrons to 20 MeV. After acceleration, the 2-5s pulse will be chopped into a
train of four 50-ns pulses with variable temporal spacing by rapidly
deflecting the beam between a beam stop and the final transport section. The
short beam pulses will be focused onto an x-ray converter target generating
four radiographic pulses within the 2-5s window. Beam instability due to
interaction with the accelerator cells can very adversely effect the beam
brightness and radiographic pulse quality. This paper describes the various
issues considered in the design of the accelerator cell with emphasis on
transverse impedance and minimizing beam instabilities.
* The work was performed under the auspices of the U.S Department of Energy
by LLNL under contract W-7405-ENG-48, and by LBNL under contract
AC03-76SF00098.
Classification Category: D04
TH4041
The Perfect Boundary Approximation Technique Facing the Big Challenge
of High Precision Mode Computation
P. THOMA, CST GmbH; B. KRIETENSTEIN*, T. WEILAND, TU-Darmstadt
Computational tools for designing accelerating structures are in use since
decades. While highly accurate methods exist for quasi two dimensional
cavities, fully three dimensional modeling with high precision is still a
"big challenge". The most widely used computer code in this area is
MAFIA. While being well known for its robustness and reliability, MAFIA
nevertheless suffers somewhat from a deficiency in being able to model very
complicated 3D-cavities with high precision for curved boundaries. The
recently developed Perfect Boundary Approximation (PBA) technique is a
promising way to improve this situation drastically. The PBA-technique
combines the easy-to-use Cartesian grids with a perfect approximation of
boundaries. With the PBA-technique, boundaries do not need to coincide with
mesh cell surfaces. Within a near-boundary cell, the exact boundary shape is
taken into account resulting in a second order algorithm for arbitrarily
shaped cavities. Thus the PBA-technique combines the good approximation
potential of FE-methods with the robustness of FD-methods. We compare MAFIA
with the PBA technique for two typical accelerator components: a 90 degree
wave guide polarization rotator and a 6 cell traveling wave cavity with
input/output coupler, including many small geometrical details. For such
structures with many non-Cartesian metallic boundaries the PBA technique can
drastically reduce the computational cost.
* Work supported in part by DESY, Hamburg.
Classification Category: D04
TH4042 (oral
poster TH3004)
Operation of the APS RF Gun*
J.W. LEWELLEN, A. LUMPKIN, S.V. MILTON, A. NASSIRI, S.J. PASKY, M.
WHITE,
ANL
The Advanced Photon Source has a thermionic-cathode rf gun system capable
of providing beam to the APS linac. The gun system consists of a 1.6-cell
thermionic-cathode rf gun, a fast kicker for beam current control, and an
alpha magnet for bunch compression and injection into the APS linac line.
This system is intended for use both as an injector for positron creation, and
as a first beam source for the Low-Energy Undulator Test Line (LEUTL) project.
The measured performance characteristics of the gun will be presented and
compared against the measured performance of the present DC-gun injector for
positron creation, and against the theoretical beam requirements for the LEUTL
line.
* Work supported by US Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy
Sciences, under Contract No. W-31-109-ENG-38.
Classification Category: T01
TH4043
Challenges of Operating a Photocathode RF Gun Injector
X.J. WANG, M. BAZIEN, I. BEN-ZVI, R. MALONE, J. SHEEHAN, T.
SRINIVASAN-RAO,
M. WOODLE, V. YAKIMENKO, BNL
The 1.6 cell photocathode RF gun developed by the BNL/SLAC/UCLA
collaboration has been in operation at the Brookhaven Accelerator Test
Facility for more than two years. Significant progress was made in the last year
to improve the stability and reliability of the photocathode RF gun injector.
We will present experiment measurements of the point stability, laser energy
stability and timing jitter. We have installed Magnesium cathode using
frictional welding, the best quantum efficiency measured is close to 1%, and
routinely operating at about 0.1%. We will also discuss the experimental
results of emittance as function of charge, and coupling between the
longitudinal and transverse emittance of photoelectron beam.
Classification Category: T01
TH4044
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4045
Suppression of the 1-MHz Beam Current Modulation in
the LEDA/CRITS Proton Source*
P. BALLEYGUIER, CEA; J. SHERMAN, T. ZAUGG, LANL
Earlier operation of a microwave proton source exhibited an approximate
1-MHz modulation in the beam current. This oscillation could cause
instabilities at higher energies in the linac, as the low-level RF control for
linac operation rolls off at 200 kHz. Tests on a dummy load show the
modulation is created by the magnetron itself: at a typical power level
required for the source operation (680W), the 1-MHz sideband level was as high
as -4 dB from carrier. Since the magnetron exhibited better behavior at higher
levels, an RF power attenuator is inserted to force the magnetron to run at a
50% higher power level for the same final power in the load. This attenuator
is made of two antennas plunged in the waveguide and connected to dummy loads
by a coaxial line. As the antennas are separated by a quarter of the guided
wavelength, mismatching effects approximately cancel each other. The antenna
length is experimentally adjusted to obtain the -1.8 dB attenuation required.
Magnetron operation at the higher power level gives a beam current spectrum
free of the 1-MHz modulation, showing the coherent beam noise is not generated
by plasma chamber phenomena.
* Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T01
TH4046
Photocathodes for the CERN CLIC Test Facility
E. CHEVALLAY, J. DURAND, S. HUTCHINS, G. SUBERLUCQ, H. TRAUTNER,
CERN
Since 1993 the CLIC Test Facility (CTF) has used laser-illuminated
Tellurium Alkali photocathodes as intense electron sources (up to 50 nC in 10
ps), for the Drive Beam of a two beam accelerator. These cathodes have been
produced and tested in our photo-emission laboratory and transported under
vacuum to the CTF. They are placed in a 3 GHz RF gun with a 100 MV/m electric
field. This RF gun produces a train of 48 pulses, each of 14 nC charge and 10
ps length. The CTF Probe Beam has used air transportable Cesium Iodide +
Germanium photocathodes in another RF gun, which produces a single pulse of
the same duration but with only 1 nC charge. The optical damage threshold in
the laser is the main limitation of energy available on the photocathode. From
an operational point of view, the photocathode lifetime is the time during
which the cathode is able to produce the nominal charge with the nominal laser
energy. After having recalled the main characteristics of the photocathodes
tested, this note describes in more detail the performance obtained in
operation. The possibility of photocathode production at the RF gun in a
simplified evaporation chamber will also be discussed.
Classification Category: T01
TH4047
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4048
Operation of the Upgraded H--Injection System of the Linac
III at DESY
C.-M. KLEFFNER, N. HOLTKAMP, M. NAGL, H. POGGENSEE, J. PETERS,
DESY
During winter 1997/98, the injection system of the H--Linac III
has been upgraded. At present two different kinds of H--sources are
operating at DESY. The new cesium-free RF ion source is planned to replace the
magnetron ion source. A new MEBT (Medium Energy Beam Transport) between two
distinct RFQ accelerators and the Alvarez accelerator of LINAC III was
installed to match the beam of each ion source to the Alvarez acceptance. This
scheme makes it possible to operate either of the ion sources with the Alvarez
linac with a miniumum of effort to switch from one to the other. The design of
the transport line also facilitates the development and tests of proposed ion
sources for deuterium and polarized protons production. After a rapid assembly
of the RFQs and ion sources as well as the new components for the MEBT, an
easy operation of the LINAC could be demonstrated. The results of measurements
in comparison to calculations will be presented.
Classification Category: T01
TH4049
Beam Transport, Acceleration and Compression Studies in the Fermilab
High-Brightness Photoinjector
J.-P. CARNEIRO, R.A. CARRIGAN, M.S. CHAMPION, A. CIANCHI, E.R. COLBY,
P.L.
COLESTOCK, H.T. EDWARDS, M.J. FITCH, J.D. FUERST, W.H. HARTUNG, M. KUCHNIR,
K.P. KOEPKE, L.K. SPENTZOURIS, FNAL; A.R. FRY, A.C. MELISSINOS, B.D. TAYLOR,
Univ. of Rochester; P. MICHELATO, D. SERTORE, C. PAGANI, INFN-Milano-LASA;
J.B. ROSENZWEIG, UCLA
Efforts are underway to produce a pulse train of up to 800 electron bunches
at the Fermilab Photoinjector, each with 8 nC of charge and a 3.5 ps rms bunch
length. The facility consists of a high quantum efficiency photocathode in a
normal conducting rf gun (1.3 GHz), a nine-cell superconducting acceleration
cavity and a magnetic bunch compressor. An initial testing phase has been
completed in which the rf gun and associated electron beam were studied in
detail. Installation of the 9-cell cavity and bunch compressor is in
progress. Once operational, the facility will be used to study beam transport
through the cavity and the physics of compression at these high brightness
levels. In the long term, the facility will be used to explore a number of
new acceleration schemes and to provide an R&D tool for a variety of new
concepts relevant to high-energy, high-intensity machines. Details of the
commissioning will be presented, and plans for future studies will be
discussed.
Classification Category: T01
TH4050
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4051 (oral
poster TH3005)
TPS Analysis of Heavy-Element Ions from
Laser-Produced Plasma
L. LÁSKA, B. KRÁLIKOVÁ, J. KRÁSA, K.
MASEK, M.
PFEIFER, K. ROHLENA, J. SKÁLA, IP ASCR; E. WORYNA, P. PARYS, J.
WOLOWSKI, IPPLM; W. MRÓZ, IO MUT; H. HASEROTH, H. KUGLER, N. LISI, H.
MAGNUSSON, R. SCRIVENS, CERN; B. SHARKOV, ITEP
The operation principle of the Thomson parabola spectrograph (TPS) is based
on the passage of ions through parallel electric and magnetic fields. It is an
excellent device to give a general overview of the charge states and the
velocity (energy) distributions of all the types of ions, produced in one
single laser shot when used with a laser ion source. A program has been
developed for the evaluation of the registered signals and for further data
processing. Using the TPS and other diagnostics based on the time-of-flight
method - ion collectors and the cylindrical electrostatic analyzer of the
energy of ions - the laser produced plasma of different heavy elements was
analyzed. As target material Ta, W, Pt, Au, Pb and Bi was chosen. The
photodissociation iodine laser system PERUN was used for this purpose and
results are compared with those obtained with the CO2 laser ion
source at CERN. Ionization and recombination processes in the expanding plasma
will be discussed, with regard to the extraction of the ions from the
expanding plasma at large distances from the target.
Classification Category: T01
TH4052
Ion Sources for the New High Current Injector at
GSI
P. SPÄDTKE, H. EMIG, K.D. LEIBLE, C. MÜHLE, H. REICH, GSI
Darmstadt
The new high current injector at GSI (HSI) will replace the existing
prestripper accelerator of Widerve type by a RFQ and an IH structure. This new
accelerator will increase the possible particle currents up to two orders of
magnitude. For the design ion Uranium, the particle current will be increased
from presently 0.1mA (U10+) to 4mA (U4+). As ion sources for such high
currents, a multi cusp ion source (for gases) or a vacuum arc ion source (for
metals) are foreseen. The existing Penning ion source, which is well
experienced for all elements of the periodic table, will be used in the future
as well and has to be improved in current performance for this new operating
regime.
Classification Category: T01
TH4053
Enhanced H- Ion Source Testing Capabilities at
LANSCE*
W. B. INGALLS, M. W. HARDY, B. A. PRICHARD, O. R. SANDER, J. E.
STELZER, R.
R. STEVENS, LANL; K. N. LEUNG, M. D. WILLIAMS, LBNL
As part of the on-going beam-current upgrade in the Proton Storage Ring
(PSR) at LANSCE, the current from the H- injector will be increased
from the
present 16-18 mA to as much as 40 mA. A collaboration between the Lawrence
Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) and the Los Alamos National Laboratory
(LANL) has been formed to develop and evaluate a new ion source. A new Ion
Source Test Stand ISTS has been constructed at LANL to evaluate candidate ion
sources. The (ISTS) has been constructed to duplicate, as closely as
possible, the 80 kV accelerating column, the beam transport, and ancillary
systems presently in use in the LANSCE H- injector, while
incorporating
additional beam diagnostics for source characterization. The construction and
commissioning of the ISTS will be described, preliminary results for the
proof-of principle ion source developed by the LBNL group will be presented,
and future plans for the extension of the test stand will be presented.
* Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy
Classification Category: T01
TH4054
Development and Test Results of the Low-Energy Demonstration Accelerator
(LEDA) Proton Injector on a 1.25 MeV CW Radio Frequency Quadrupole*
J. D. SHERMAN, G. BOLME, L. HANSBOROUGH, D. HODGKINS, E. MEYER, J. D.
SCHNEIDER, H. V. SMITH, JR., M. STETTLER, R. R. STEVENS, JR., M. THUOT, T.
ZAUGG, LANL; A. ARVIN, A. S. BOLT, M. RICHARDS, SRS; P. BALLEYGUIER,
CEA/Bruyeres le Chatel; J. KAMPERSCHROER, General Atomics
The LEDA 75-keV proton injector is being developed for tests of
high-current (100 mA) CW linacs. The injector comprises a microwave proton
source and a space-charge neutralized magnetic low-energy beam transport
system (LEBT). The LEDA injector has been configured to provide flexible
50-keV beam matching into a cw 1.25 MeV radio frequency quadrupole (RFQ)
brought from Chalk River Laboratories [1]. The LEBT has two solenoid focus
magnets separated by 117 cm. Between the solenoids are two steering magnets
and diagnostic stations for measuring the beam current, profile, and position.
The LEBT can match any reasonable ion source proton beam extracted into the
RFQ. The ion source extraction system was modified to a 50 keV triode to test
the injector/RFQ system. Beam matching tests showed that injector-RFQ
transmission is 90% for 50-mA RFQ current. At the RFQ design current of 75
mA the beam transmission decreased to 80 - 85%. Aggressive injector tuning
led to 100-mA beam accelerated through the RFQ. Design details for the
50-keV beam operation, and injector beam matching studies will be
presented.
*Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
[1] J. D. Schneider et al., "Installation of a CW Radiofrequency Quadrupole
Accelerator at Los Alamos National Laboratory," Proc. of LINAC94, p.
149.
Classification Category: T01
TH4055
Operation of a Microwave Proton Source in Pulsed
Mode*
T. ZAUGG, C. ROSE, J. D. SCHNEIDER, J. SHERMAN, R. STEVENS, JR.,
LANL
Initial beam operation of the cw radio-frequency-quadrupole (RFQ) built for
the Low Energy Demonstration Accelerator (LEDA) project requires the injection
of a 75-keV, pulsed, H+ beam with a rise and fall time less than 10
microseconds and a pulse width from 100 microseconds to 1 millisecond at a
repetition rate up to 10 Hz. The ion source for the accelerator is a microwave
proton source driven by a 2.45 GHz magnetron. Pulsed beam from the injector is
accomplished by modulation of the magnetron tube current. The magnetron
provides microwave pulses to the ion source, and a medium-bandwidth,
extraction power supply accelerates the H+ ion beam using a four-electrode
extractor. A similar ion source with a three-element extractor operating at 50
kV has also been tested with this magnetron modulator. We report the results
of modulating the ion source microwave power and extracting a pulsed proton
beam using both a triode and a tetrode extractor.
*Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T01
TH4056
Physics Design of the DARHT Electron Beam Injector*
E. HENESTROZA, UC-Davis; S. YU, S. EYLON, W. FAWLEY, LBNL
An injector for the for the second phase of the Dual-Axis Radiographic
Hydrotest Facility (DARHT) is been designed at LBNL. The proposed injector
consists of a single gap diode extracting 4 kAmps, 3.0 MV electrons from a
thermionic dispenser cathode and powered through a high voltage ceramic
insulator column by a Marx generator. The key issues in the design are the
control of beam quality to meet the DARHT final focus requirements and to
minimize high-voltage breakdown risks. We will present the physics design and
beam dynamics simulations of the injector.
*The work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy
under contract AC03-76SF00098.
Classification Category: T01
TH4057
The Frankfurt H- Source for European Spallation Source
(ESS)
K. VOLK, A. MAASER, H. KLEIN, IAP-Univ. of Frankfurt
For the European Spallation Source (ESS) two ion sources are required, each
delivering 70 mA of H- ions during a 1.2 ms pulse and at a repetition
rate of
50 Hz. In Frankfurt a H- volume source, based on the HIEFS (high
efficiency
source) is being developed and tested. The source consists of a cesium seeded
multicusp plasma generator, where negative ions are produced via volume and
surface processes. During the last year, improvements of the cesium injection
method enhance the beam current density up to already 120 mA/cm2.
Up to now, a H- beam current of 80 mA has been extracted using an
aperture
radius of 5 mm.
The paper reports about the recent developments of the Frankfurt
H- source.
After a description of the ion source and the experimental setup, measurements
of the beam current density, the electron to H- ratio, the lifetime
of the
source and an emittance estimation will be presented.
Classification Category: T01
TH4058
Implementation of Improved Interactive Image Analysis at the Advanced
Photon Source (APS) Linac*
N. ARNOLD, W. BERG, S. BIEDRON, A. LUMPKIN, S. MILTON, M. WHITE, B.
YANG, ANL
An improved image analysis system based on commercially available data
visualization software (IDL) allows a convenient interaction with image data
while still providing calculated beam parameters at a rate of up to 2 Hz.
Image data are transferred from the IOC to the workstation via EPICS channel
access, thus, creation of a custom EPICS record was necessary to overcome the
channel access limit of 16k bytes per array. The user can conveniently
calibrate the screens, capture background images, acquire and average a series
of images, and specify several other filtering and viewing options. The images
can be saved in an APS-standard format (SDDS), allowing for rapid
postprocessing of image data by numerous other software tools.
* Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy
Sciences, under Contract No. W-31-109-ENG-38.
Classification Category: T02
TH4059 (oral
poster TH3006)
Non-Interceptive Emittance Measurement of a High
Intensity Beam at Low Energy
P.-Y. BEAUVAIS, R. FERDINAND, R. GOBIN, B. POTTIN, CEA/Saclay
A CW Electron Cyclotron Resonance source has been constructed at CEA-Saclay
and is now under test. The aim is to reach a 100 mA proton current at 95 keV
with an rms normalized emittance smaller than 0.2 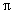 .mm.mrad and
a very high
reliability. In order to match this beam into the Radio Frequency Quadrupole
linac (RFQ), its characteristics have to be monitored on-line. An emittance
measurement unit (EMU) located close to the RFQ entrance is a very powerful
diagnostic tool. We developed a non-interceptive EMU based on the video
analysis of the residual gas illumination. Methods and results are presented
and discussed.
.mm.mrad and
a very high
reliability. In order to match this beam into the Radio Frequency Quadrupole
linac (RFQ), its characteristics have to be monitored on-line. An emittance
measurement unit (EMU) located close to the RFQ entrance is a very powerful
diagnostic tool. We developed a non-interceptive EMU based on the video
analysis of the residual gas illumination. Methods and results are presented
and discussed.
Classification Category: T02
TH4060
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4061
Bunch Length and Velocity Measurement of the JHP-RFQ Beam with INR
BLVD
A. V. FESCHENKO, V. A. GAIDACH, S. A. KRIOUKOV, A. A. MENSHOV, P. N.
OSTROUMOV,
INR RAS; A. UENO, KEK
The bunch length and velocity of a beam accelerated with the 432-MHz, 3-MeV
JHP-RFQ (Japanese Hadron Project - Radio Frequency Quadrupole) linac were
measured by using a Bunch Length Velocity Detector (BLVD) developed by INR.
The measured velocity (0.08002 ±
0.00016)c as well as bunch shape showed a good agreement with the simulation
results. The longitudinal profiles of the bunch have been measured for various
setting of the RFQ. The bunch shapes of H-minus beam as well as proton beam
(produced by the stripping of H-minus ions) have been studied. Although the
BLVD has been designed for measurement of beam core (~99% of particles) the
accurate study of beam halo particle has been done. An almost uniformly
distributed background noise signal in every longitudinal position was
observed. The amount of the integrated noise signal was about 1% of the beam
intensity. A possible source of the noise is analyzed.
Classification Category: T02
TH4062
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4063
Roll Bar X-ray Spot Size Measurement Technique*
R. A. RICHARDSON, T. L. HOUCK, LLNL
Dynamic effects such as backstreaming ions and electron-beam-plasma
interactions can adversely effect the x-ray spot behavior of advanced,
multishot, radiography machines. A time dependent x-ray spot size measurement
is therefore critical to understanding beam target interaction physics. The
so-called roll bar measurement uses a heavy metal material, which is optically
thick to X-rays, to form a shadow of the x-ray spot. This spot is a result of
the interaction of the energetic electron beam with a high Z target. The
material (the "roll bar") has a slight radius to avoid alignment
problems. A beam profile is assumed (or measured by other means) and the
equivalent x-ray spot size is calculated from the x-ray shadow cast by the
roll bar. Typically a radiographic film is exposed over the duration of the
beam pulse and the shadow is analyzed for a time integrated measurement. This
paper explores various techniques to convert the x-rays to visible photons
that can be imaged using a gated camera or streak camera for time evolved
x-ray spot size. Data will be presented from the measurements on the ETA II
induction linac.
*Work performed under the auspices of the U. S. Department of Energy by
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under contract W-7405-ENG-48.
Classification Category: T02
TH4064
Development of Nanometer Resolution C-band Radio
Frequency Beam Position Monitors in the Final Focus Test Beam*
T. SLATON, G. MAZAHERI, SLAC; T. SHINTAKE, KEK
Using a 47 GeV electron beam, the Final Focus Test Beam (FFTB) produces
vertical spot sizes around 70 nm [1]. These small beam sizes introduce an
excellent opportunity to develop and test high resolution Radio Frequency Beam
Position Monitors (RF-BPMs). These BPMs are designed to measure pulse to
pulse beam motion (jitter) at a theoretical resolution of approximately
1 nm [2]. The beam induces a TM110 mode with an amplitude linearly
proportional to its charge and displacement from the BPM's (cylindrical
cavity) axis. The C-band (5712 MHz) TM110 signal is processed and
converted into beam position for use by the Stanford Linear Collider (SLC)
control system. Presented are the experimental procedures, acquisition, and
analysis of data demonstrating resolution of jitter near 25 nm. With the
design of future e+e- linear colliders requiring spot
sizes close to 3 nm [3], understanding and developing RF-BPMs will be
essential in resolving and controlling jitter.
*Work supported by the Department of Energy, contract
DE-AC03-76SF00515.
[1] D. L. Burke, et al., SLAC-PUB-6609, Proceedings of EPAC 94; V. E.
Balakin, et. al., SLAC-PUB-95-6691, Phys.Rev.Lett.74:2479-2482,1995; V.A.
Alexandrof, et al., KEK-PREPRINT-95-31, IEEE PAC 1995:2742-2746.
[2] S.C. Hartman, et al., SLAC-PUB-95-6908, IEEE PAC 1995:2655-2657.
[3] R.H. Siemann, SLAC-PUB-6244, IEEE PAC 1993:532-536.
Classification Category: T02
TH4065
A High Peak Power S-band Switching System for the Advanced Photon
Source (APS) Linear Accelerator (Linac)*
A. E. GRELICK, N. ARNOLD, S. BERG, Y. W. KANG, R. L. KUSTOM, A.
NASSIRI, J.
NOONAN, M. WHITE, ANL
An S-band linear accelerator is used in the Advanced Photon Source injector
and additionally will be used to support a low-energy undulator test line
(LEUTL) and a free-electron laser. To provide optimum availability for these
uses, an additional modulator-klystron subsystem has been built and a
waveguide switching and distribution subsystem is being constructed. The
combined subsystems provide a hot spare for any of the five S-band
transmitters that power the linac and have been given the additional function
of powering an rf gun test stand whenever they are not otherwise needed. The
design considerations for the waveguide switching subsystem, topology
selection, timing, control, and protection provisions are described.
* Work supported by the U. S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy
Sciences under Contract No. W-31-109-ENG-38.
Classification Category: T04
TH4066 (oral
poster TH3007)
Performance of an S-Band Klystron at an Output Power
of 200MW
S. CHOROBA, J. HAMEISTER, S. JARYLKAPOV*, DESY
In order to provide RF power to the accelerating sections of a future
S-Band linear collider, klystrons delivering 150MW of output power at a
frequency of 2.998GHz are required. Two S-Band klystrons with a nominal output
power of 150MW at a pulse duration of 3microsec. and a repetition rate of
50Hz were developed in a collaboration between SLAC, Philips, TH Darmstadt and
DESY [1]. They were built and successfully tested at SLAC in 1994 and 1995 and
then shipped to DESY to feed the accelerating sections of the S-Band test
facility linac. In order to explore their power potential one of the klystrons
was operated at an even higher output power of more than 200MW at the test
facilty. HV pulses up to 610kV at a current of 780A were applied to the
klystron cathode. This paper reports the results of the measurements of the
various parameters of the klystron at this power level (e.g. output power,
efficiency, perveance). It describes the performance and the limitations of
the klystron in this power range.
*on leave from INR, Moscow
[1] D. Sprehn, G. Caryotakis, R.M. Phillips, "150-MW S-Band Klystron
Program at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center," Proceedings of the Third
Workshop on Pulsed RF Sources for Linear Colliders (RF96), KEK Proceedings 97-1,
p 91.
Classification Category: T04
TH4067
Overview of the APT RF Power Distribution System*
M. MCCARTHY, General Atomics; M. LYNCH, LANL; T. OVERETT, General
Atomics; D. REES, LANL; G. SPALEK, J. TOOKER, General
Atomics
The Accelerator Produced Tritium (APT) project requires a linac of nearly a
kilometer in length. Accelerating potential for the 100 mA proton beam is
provided by 350 and 700 MHz klystrons. The radio frequency power distribution
for the 160 1MW klystrons has a wide range of design requirements and
constraints. Efficient transport, control of phase, control of fault events,
thermal dissipation and coupling considerations will be discussed. A
description of the currently proposed configurations will be presented.
* Work supported by U.S. DOE contract: DE-AC04-96AL89607.
Classification Category: T04
TH4068
A Conceptual Design of RF System in the NSP Superconducting Linac at
JAERI
E. CHISHIRO, Y. HONDA, Y. TOUCHI, N. OUCHI, K. HASEGAWA, J. KUSANO, M.
MIZUMOTO, JAERI
We have performed a design study work of a high intensity proton
accelerator proposed for Neutron Science Project (NSP) at JAERI. The NSP
accelerator will consist of RFQ, DTL and superconducting (SC) linac. It should
be operated both in pulse and CW for demands in the application. The SC linac
accelerates hydrogen ion beams from 0.1 GeV to 1.5GeV. An accelerating
structure of the SC linac is divided into several beta sections, since the
particle velocity varies along the linac. The SC structure with 8 different
beta section suppresses the beam emittance growth and reduces the linac
length. This linac has 284 cavities and the length of 690m. Number of cavities
driven by an amplifier is set to 4. One of those cavities has the surface peak
field of 16MV/m and the RF parameters of 4 cavities are adjusted to distribute
the same RF power. For a pulse operation with the peak beam current of 30mA,
the peak power of 158kW/cav. is required at the high-beta end. The other hand,
the power of 47kW/cav. is required for the CW operation accelerating a beam
current of 5.33mA. The total RF powers for pulse and CW operation are 29MW and
8.6MW, respectively.
Classification Category: T04
TH4069 (oral
poster TH3008)
Development of the X-band Klystron Modulator at KEK
M. AKEMOTO, S. ANAMI, H. MIZUNO, S. TOKUMOTO, KEK; T. MAJIMA, Y.
KOBAYASHI,
IHI
Two kinds of modulators with a Blumlein pulse-forming network (PFN) to
drive a 65 MW X-band pulsed klystron for the main linac of linear collider are
under development at KEK. The first modulator consists of a 1:8 step up pulse
transformer, and two PFN's, a thyratron switch tube and a resonant charging
circuit which are housed in air. The second modulator consists of two PFN's, a
1:7 step up pulse transformer, a thyratron switch tube and a resonant charging
circuit which are all housed in a cylindrical oil tank which also mounts the
klystron. This paper describes the performance of these modulators. The
improvements of the performance of the PFN and the pulse transformer are also
presented.
Classification Category: T04
TH4070
A New RF System for the Debuncher at the KEK 40-MeV Proton
Linac
Z. IGARASHI, E. TAKASAKI, T. TAKENAKA, K. NANMO, KEK
The RF system for the debuncher was renewed to an all solid state amplifier
last summer. The amplifier containing one hundred and eight power transistors
on its output stage can deliver a 20kW stably at 201MHz, so the momentum
spread of the linac beam can be decreased less than 1%. This new rf system
for the debuncher and its operational results are described.
Classification Category: T04
TH4071
C-band 50 MW Klystron Using Traveling-Wave Output Structure
Y. OHKUBO, Toshiba Co.; T. SHINTAKE, N. AKASAKA, H. MATSUMOTO, KEK
The second tube of the C-band 50 MW klystron : TOSHIBA E3746 #2 has been
developed in the course of the C-band rf-system R&D [1]. It uses a
 /2 mode traveling-wave structure in the output-circuit in
order to
enhance the power-conversion efficiency. The three-cell disk-loaded structure
was analyzed by the coupled-resonator model, and parameterized in a 3 x 3
matrix form. The electrical performance at a hot-condition was calculated by a
particle-in-cell simulation code: FCI, which predicted a power efficiency of
48%. This paper describes the design details and the experimental results.
/2 mode traveling-wave structure in the output-circuit in
order to
enhance the power-conversion efficiency. The three-cell disk-loaded structure
was analyzed by the coupled-resonator model, and parameterized in a 3 x 3
matrix form. The electrical performance at a hot-condition was calculated by a
particle-in-cell simulation code: FCI, which predicted a power efficiency of
48%. This paper describes the design details and the experimental results.
[1] T. Shintake et al., "C-band RF Main Linac System for e+e- Linear
Colliders," EPAC96, Barcelona Spain, July 1996.
Classification Category: T04
TH4072
Efficiency Enhancement of RF-Pulse Compressor for C-band Linear
Collider
M. YOSHIDA, Univ. of Tokyo; T. SHINTAKE, N. AKASAKA, H. MATSUMOTO,
KEK
Utilizing the energy in the front part of the HV-modulator pulse, the power
gain of the rf-pulse compressor will be enhanced. To compensate the phase slip
in the klystron due to the voltage rise, we apply the phase modulation on the
rf signal at the klystron input. A computer simulation predicted a power gain
higher than 4.0 at the compression factor of 5, therefore the effective
efficiency will exceed 80%. In the C-band linear collider, we use a three-cell
coupled-cavity as the rf pulse compressor [1]. The phase modulator also
compensates the voltage-swing associated with the coupled-cavity resonances
and produces a flat-pulse output required for multi-bunch beam acceleration.
This paper describes the figure of merit in this scheme as well as a
possibility to apply the super-conductive cavity in the compressor.
[1] T. Shintake et al., "Development of C-band RF Pulse Compression
System for e+e- Linear Collider," PAC97, Vancouver, May 1997.
Classification Category: T04
TH4073
Results and Lessons Learned from Conditioning 1 MW CW
350 MHz Coaxial Vacuum Windows
K. CUMMINGS, R. CORDOVA, D. REES, W. ROYBAL, LANL; S. RISBUD,
UC-Davis; D.
WILCOX, EEV
The reliability of the radio frequency (RF) windows on the Low Energy
Demonstration Accelerator (LEDA) is critical to the success of the Accelerator
Production of Tritium Program (APT). On the APT machine there will be over
1000 windows, each passing on the order of 250 kW of CW RF power. This power
level is well above power levels historically used in RF windows. Based on the
high-power RF test results of the RF window prototypes from vendors, the
coaxial windows made by EEV Ltd. of Chelmsford, England, were selected for
LEDA. This paper describes the high-power RF testing of the 15 EEV coaxial
windows. The RF window diagnostic equipment, data acquisition system and test
stand are described. The results of the high power RF testing of the windows
are presented. The successes and failures in the conditioning, manufacturing
and testing techniques of the windows are presented. The conditioning
timeline, power profile and the conditioning waveform are also discussed.
Classification Category: T04
TH4074
Solid State Power Amplifier as 805 MHz Master Source for LANSCE
Side-Coupled-Cavity Linac*
J. LYLES, J. DAVIS, LANL
From 100 to 800 MeV, the LANSCE proton linac receives RF power from
forty-four 1.25 MW klystrons at 805 MHz. A single master RF source provides a
continuous high level phase and amplitude reference signal to drive the
klystrons along the 731 meter-long linac through a coaxial transmission line.
A single point failure of this system can deenergize the entire SCCL RF plant.
The authors replaced a physically large air-cooled tetrode amplifier with a
compact water-cooled unit based on modular amplifier plates developed at
LANSCE. Each 800 Watt plate utilizes eight push-pull bipolar power transistor
pairs operated in class AB. Four plates can easily provide the 2800 watt
reference carrier from the low level RF system. A radial splitter and combiner
parallels the modules. This amplifier has proven to be completely reliable
after a year of operation without failure. A second unit was constructed and
installed for redundancy, and the old tetrode system was removed in 1998. The
compact packaging for cooling, DC power, impedance matching, RF
interconnection, and power combining met the electrical and mechanical
requirements. CRT display of individual collector currents and RF levels is
made possible with built-in samplers and a VXI data acquisition unit.
*Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T04
TH4075
LEDA LLRF Control System Characterization
A.H. REGAN, LANL; P. BALLEYGUIER, CEA; C.D. ZIOMEK, ZTEC
The Low Energy Demonstration Accelerator (LEDA) for the Accelerator for the
Production of Tritium (APT) project will be built at Los Alamos National
Laboratory. The low-level RF (LLRF) control system portion of this
accelerator must perform many functions, of which the primary one is
controlling the RF fields in the accelerating cavities. Plans have been made
to provide for on-line characterization of the LLRF control system and the
complete RF system through use of stimulus and response buffers, and a digital
signal processor built into the field control system electronics. The purpose
of this circuitry is to characterize the behavior of the entire RF system
(klystron, waveguides, high power splitters, accelerator cavity, etc.). This
characterization feature can be used to measure the performance of the closed
loop system with respect to the open loop system, to provide an automated way
to set loop parameters, to determine the cavity Q-curve, and to detect any
abnormal behavior in the RF chain. The types of measurements include
frequency and time-domain responses to given perturbations, amplitude
modulations, etc. This paper will discuss types of algorithms that can be
implemented and present a description and block diagram of the electronics to
be used.
Classification Category: T04
TH4076
LEDA RF Distribution System Design and Component Test
Results*
W. T. ROYBAL, D. E. REES, LANL; L. TOOLE, SRS; M. MCCARTHY,
General Atomics
The 350 MHz and 700 MHz RF distribution systems for the Low Energy
Demonstration Accelerator (LEDA) have been designed and are currently being
installed at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Since 350 MHz is a familiar
frequency used at other accelerator facilities, most of the major high-power
components were available. The 700 MHz, 1.0 MW, CW RF delivery system
designed for LEDA is a new development. Therefore, high-power circulators,
waterloads, phase shifters, switches, and harmonic filters had to be designed
and built for this application. The final Accelerator Production of Tritium
(APT) RF distribution systems design will be based on much of the same
technology as the LEDA systems and will have many of the RF components tested
for LEDA incorporated into the design. Low power and high-power tests
performed on various components of these LEDA systems and their results are
presented here.
* Work supported by the US Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T04
TH4077
A Thermal Analysis and Optimization of the APT 210 kW RF Power
Coupler*
J.A. WAYNERT, F.C. PRENGER, LANL
This paper presents the thermal analysis and heat load optimization of the
210 kW, 700 MHz RF power coupler (PC) for the Accelerator Production of
Tritium (APT). The PC is a co-axial design with RF power transmitted in the
annular region between two concentric cylinders. Thermally, the PC represents
a link from room temperature to the superconducting niobium cavities operating
at 2 K. The PCs represent the second largest thermal load on the 2 K system,
only the cavities generate a larger heat load. Thus, the objective of the
analysis is to minimize the total refrigeration input power subject to
manufacturability and availability constraints and refrigeration plant capital
and operating cost concerns. The analysis includes all the major heat
transfer mechanisms: conduction, RF joule heating in normal and
superconducting materials, infra-red radiation, and, forced and natural
convection cooling of the inner and outer conductors. A performance
comparison is given for one and two single point thermal intercepts, versus a
counter-flow heat exchanger on the outer conductor. The benefits of reducing
the operating temperature of the center conductor are discussed. The
variation in thermal performance of the inner and outer conductors with
operating modes is also presented.
* Research supported through U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T04
TH4078
A Multi-Moded RF Delay Line Distribution System for the Next Linear
Collider (NLC)
S. G. TANTAWI, C. ADOLPHSEN, G. BOWDEN, Z. D. FARKAS, J. IRWIN, K. KO, N.
KROLL, T. LAVINE, Z. LI, R. LOEWEN, R. MILLER, C. NANTISTA, R. D. RUTH, J.
RIFKIN, A. E. VLIEKS, P. B. WILSON, J. WANG, SLAC
The Delay Line Distribution System (DLDS) is an alternative to conventional
pulse compression which enhances the peak power of an rf source while matching
the long pulse of that source to the shorter filling time of the accelerator
structure. We present a variation on that scheme that combines the parallel
delay lines of the system into one single line. The power of several sources is
combined into a single waveguide delay line using a multi-mode launcher. The
output mode of the launcher is determined by the phase coding of the input
signals. The combined power is extracted using several mode extractors, each of
which extracts only one single mode. Hence, the phase coding of the sources
controls the output port of the combined power. The power is, then, fed to the
local accelerator structures. We present a detailed design of such a system,
including several implementation methods for the launchers, extractors, and
ancillary high power rf components. The system is designed so that it can handle
the 600 MW peak power required for the second stage of the NLC design, while
maintaining high efficiency.
Classification Category: T04
TH4079
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4080
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4081
DXRL Fabrication and Measurement of Millimeter Wave Accelerating
Structures *
Y. KANG, J. SONG, A. NASSIRI, R. KUSTOM, ANL
Millimeter-wave accelerating cavity structures have been manufactured using
the deep x-ray lithography (DXRL) technique. So far two prototypes have been
made: a 30-cell constant impedance structure for 108-GHz and a 66-cell
constant gradient structure for 94-GHz. These prototypes were designed and
built to study the feasibility of building precision traveling wave cavities
operating at millimeter-wavelength frequencies for compact linear
accelerators. Basic radio frequency and mechanical properties have been
measured for future improvement. Millimeter-wave characteristics were checked
using an HP8510C 26-GHz vector network analyzer setup with a frequency
up-converter and a frequency down-converter before and after a test cavity
structure.
* Work supported by U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy
Sciences under Contract No. W-31-109-ENG-38.
Classification Category: T05
TH4082
Niobium Spoke Cavities for a Superconducting
Light-ion Linac
K. W. SHEPARD, ANL; J. R. DELAYEN, TJNAF; M. KEDZIE, ANL; C. PILLER,
TJNAF
This paper reports the development of 350 MHz niobium superconducting
cavities for accelerating particles over the velocity range 0.2 < v/c <
0.6. Such cavities could be used to form a linac of exceptional flexibility,
capable of efficiently accelerating beams of protons, deuterons, or any of a
wide range of light ions at intensities sufficient for a production beam for a
radioactive beam facility. Results of numerical modeling for several
resonator geometries are discussed, and the design and construction status of
prototype niobium cavities is presented.
Classification Category: T05
TH4083
A Tapered Damped Accelerating Structure for
CLIC
M. DEHLER, I. WILSON, W. WUENSCH, CERN
A new 30 GHz multibunch accelerating structure incorporating both damping
and detuning has been designed for the Compact LInear Collider (CLIC). Each
cell of the 150-cell structure is damped by its own set of four radial
waveguides resulting in a Q of 16 for the lowest dipole mode. A simple linear
taper of the beam-pipe dimension provides a detuning frequency spread of 2 GHz
(5.4%). Predictions of the transverse wakefield levels in this structure have
been made using both uncoupled, and two-band coupled equivalent circuit models
with non-perfect loads. The short-range wakefield has been calculated to be
about 1000 V/(pC.mm.m) decreasing to less than 1% at the second bunch and with
a long time level below 0.1%. The fundamental mode properties have been
calculated using general expressions derived for linearly-tapered group
velocity structures.
Classification Category: T05
TH4084
 /2 Interleaved Cavity Developments for the Muon
Experiment*
/2 Interleaved Cavity Developments for the Muon
Experiment*
J.N. CORLETT, LBNL; H.G. KIRK, BNL; D. LI, LBNL; A. MORETTI, FNAL;
W.C.
TURNER, LBNL; R.B. PALMER, Y. ZHAO, BNL
In this paper we discuss the development of a  /2
interleaved standing
wave linac for the proposed Muon cooling experiment. The nominal beam momentum
is 186 MeV/c (ß=0.87). Each Muon cooling channel section contains a 1.3m rf
accelerating linac separated by 0.64m of liquid hydrogen absorbers immersed in
an alternating superconducting solenoidal magnetic transport line. Instead of
conventional open cavity beam apertures, the 805 MHz linacs have thin Be
windows covering iris apertures. The accelerating cavities closely resemble
pillbox cavities and have little or no field enhancement due to iris aperture
corners. Further, since the peak field is on the axis, the shunt impedance is
about a factor 2 larger than conventional designs. It is also proposed to cool
the cavity to liquid nitrogen temperature to reduce the losses and therefore,
also increase the shunt impedance. Our
/2
interleaved standing
wave linac for the proposed Muon cooling experiment. The nominal beam momentum
is 186 MeV/c (ß=0.87). Each Muon cooling channel section contains a 1.3m rf
accelerating linac separated by 0.64m of liquid hydrogen absorbers immersed in
an alternating superconducting solenoidal magnetic transport line. Instead of
conventional open cavity beam apertures, the 805 MHz linacs have thin Be
windows covering iris apertures. The accelerating cavities closely resemble
pillbox cavities and have little or no field enhancement due to iris aperture
corners. Further, since the peak field is on the axis, the shunt impedance is
about a factor 2 larger than conventional designs. It is also proposed to cool
the cavity to liquid nitrogen temperature to reduce the losses and therefore,
also increase the shunt impedance. Our  /2 interleaved cavity
design is
essentially two chains of side coupled
/2 interleaved cavity
design is
essentially two chains of side coupled  /2 cavities
interleaved to form continuous chains of accelerating cells on the beam axis.
Each accelerating
cell has a phase advance of
/2 cavities
interleaved to form continuous chains of accelerating cells on the beam axis.
Each accelerating
cell has a phase advance of  /2 and therefore, a favorable
transit time
factor. This paper will discuss the design of the cavity, MAFIA calculations,
low-power rf model cavity measurements, low-temperature effects with Be
windows, design of high-power rf test models and proposed high rf power test
facility.
/2 and therefore, a favorable
transit time
factor. This paper will discuss the design of the cavity, MAFIA calculations,
low-power rf model cavity measurements, low-temperature effects with Be
windows, design of high-power rf test models and proposed high rf power test
facility.
*Work supported by th e U.S. Department of Energy under contract No.
DE-AC02-76CH03000.
Classification Category: T05
TH4085
Scale Room Temperature Model of the Superconducting RFQ1 for the PIAVE
Linac
V. ANDREEV, G. BISOFFI, M. COMMUNIAN, A. LOMBARDI, A. PISENT, A.M.
PORCELATO, INFN-LNL; T. SHIRAI, ICR-Kyoto University
The new injector PIAVE (Positive Ion Accelerator for Very-low Energy) will
use two bulk niobium (Nb) superconductng RFQs (SRFQ1 and SRFQ2), which will be
operated at 80 MHz. The electrode length of SRFQ1 is about twice as long as
SRFQ2 thus requiring an EBW vacuum chamber larger than the previosly available
one. A principal decision was hence taken to split the electrodes and the tank
into two parts. A half-scale room temperature model was built at LNL in order
to test RF characteristic of the structure and to determine its exact
dimensions. Results of the model measurements and MAFIA code simulations are
presented.
Classification Category: T05
TH4086
Equivalent Lumped Circuit Study for the Field Stabilization of a Long
Four-vanes RFQ
A. PISENT, INFN-LNL; R. CELENTANO, INFN-LNL and University of Naples;
R.
ZENNARO, INFN-LNL and University of Ferrara
The possibility to design an RFQ long respect to the rf wavelength is very
important for the feasibility of linacs with different applications, from the
high power CW linacs for neutron production to the low power high frequency
linacs proposed for hadrotherapy. In particular INFN has been funded for the
study of the critical parts of a waste transmutation linac. In this framework
the field stabilization of a 352 MHz RFQ has been studied, using the LANL
resonant coupling technique; an equivalent lumped circuit approach has been
used, and compared with MAFIA simulations. Based on the results of these
studies an aluminum model (1:1 scale, 0.04 mm tolerances) has been built and
we are now ready for the test of the tuning procedure.
Classification Category: T05
TH4087
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4088
The Possibility of Multipactor Discharge in Coupling Cells of Coupled
Cells Accelerating Structures
V.V. PARAMONOV, S.G. TARASOV, INR RAS
The multipactor discarge takes place at low values of electric rf field.
Operating values of the field in accelerating cells are usually much more
higher than the upper threshold of the discharge and this phenomenon takes
place during structure conditioning. In operating regime, during rf pulse,
weak electric field, linearly decreasing from the point of the rf drive to the
end of the cavity, exists in coupling cells to provide rf power flux along the
cavity. Depending on cavity operating regime and coupling cells parameters,
the value of this field can be in limits of the discharge. In this paper
parameters of coupling cells for side coupled, on-axis coupled and annular
coupled structures are considered and estimations for electric field are
given. Results of numerical simulations of the discharge in coupling cells are
presented.
Classification Category: T05
TH4089
Progress Work in a 27 MHz Heavy Ion RFQ
V. ANDREEV, D. KASHINSKY, A. KOLOMIETS, S. MINAEV, V. PERSHIN, R.
VENGROV,
V. ZVIAGINTSEV, S. YARAMISHEV, ITEP; G. PARISI, IAP-Univ. of Frankfurt
A 27 MHz heavy ion RFQ is now under construction at ITEP. It based on new
ring-connected resonant structure. This structure is low frequency version of
previously described "four-ladder" structure. The RFQ has been designed for
acceleration of heavy ions with charge to mass ratio 1/60 to energy 110 keV/u.
At present the manufacture of the structure is completed, RFQ is assembled and
installed into a vacuum tank. The RF measurements confirm the expected
parameters calculated by MAFIA and SOPRANO codes - resonant frequency, very
reliable mode separation and perfect electrical field distribution. The
carried out numerical simulations and experimental results show that given RFQ
type is considerably promising candidate for use as initial part of high
current heavy ion linac for HIF.
Classification Category: T05
TH4090
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4091
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4092
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4093
Calculations of External Coupling to a Single Cell RF
Cavity
D. LI, R. RIMMER, S. KOSTA, LBNL
A method is proposed to calculate the intrinsic and external Q values of a
cavity coupled to a waveguide using MAFIA code in time domain. Typical methods
used for the Q calculation in time domain are also reviewed. The method works
efficiently for high Q cavities with coupling strengths close to critical
coupling case. Applications of the method to a single cell rf cavity coupled
to a waveguide are presented. The comparisons between the simulation and
experimental results are given for a set of different coupling iris apertures.
Classification Category: T05
TH4094
Mechanical Design, Construction and Alignment of the ISAC RFQ
Accelerator at TRIUMF
G. STANFORD, D. PEARCE, R. L. POIRIER, TRIUMF
The ISAC RFQ is an 8 meter long, 4-rod split-ring structure operating at 35
MHz in CW mode. The rods are vane-shaped and supported by 19 rings spaced 40
cm apart. The stringent, ± 0.08 mm, quadrature positioning tolerance of the
four rod electrodes over the 8m length was met by adopting a design philosophy
based on manufacturing 19 identical rings and mounting them on precision
ground platens which are accurately aligned in the vacuum tank prior to ring
instalation. The accurately made components are assembled on a special
assembly fixture and the electrode mounting surfaces are final machined in a
jig after ring assembly using non-contact electrical discharge machining
(EDM). The basic design of the ring is unique in that the RF surfaces have
been de-coupled from the mechanical support structure to improve dynamic
stability. The vacuum tank is also unique in that it is square in
cross-section and split diagonally to obtain full unobstructed side access to
the RFQ modules. The three dimension theodilite intersection method was used to
accurately align two platen bases in the tank to allow 7 of the 19 rings to be
installed in the first section of the 8m long vacuum tank.
Classification Category: T05
TH4095
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4096
Engineering Design of the APT Cryomodules*
B.M. CAMPBELL, J.P. KELLEY, R. VALICENTI, J.A. WAYNERT, LANL
The high energy section of the Accelerator Production of Tritium (APT)
linac uses superconducting radio frequency (SRF) cavities to accelerate a 100
mA proton beam from 211 MeV to 1700 MeV. Since SRF cavities can accept
protons over a wide range of energy, only 2 different beta cavities are
required; however 3 different length cryostats, or cryomodules, are required
primarily to accommodate the changing magnet focussing lattice. A modular
approach that will reduce the engineering and design effort required to
produce these cryomodules has been adopted. The cavities will be cooled in a
2.15 K superfluid helium bath similar to that used by the Continuous Electron
Beam Accelerator Facility (CEBAF). The comparatively short development time
span for these cryomodules has led us to adopt many other design features from
proven operating cryomodules. What sets the APT cryomodules apart is the
comparatively high RF power. Although nearly 100% of the power is delivered
to the beam, the RF losses occurring in the cavities and power couplers still
place a large heat load on the refrigeration system. Reducing RF losses is a
high design priority for these cryomodules, and analytical methods developed
to define and minimize these losses will be described.
*Research supported through U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T06
TH4097 (oral
poster TH3009)
Progress of APT Superconducting Linac Engineering
Development*
K. C. D. CHAN, B. M. CAMPBELL, R. C. GENTZLINGER, J. P. KELLEY, B.
RUSNAK,
H. SAFA**, LANL
We initiated a program to develop superconducting (SC) RF for high-power
proton linacs. These linacs are useful in accelerator-driven transmutation
technologies and the Accelerator Production of Tritium (APT) Project. We are
developing multicell niobium cavities with elliptical-cell shapes at 700 MHz.
These cavities, unlike most elliptical cavities for electron accelerators, are
designed to accelerate protons at beta less than 1. Coaxial power couplers
are being developed to transmit high (250 kW) CW RF power to the cavities.
The couplers will be tested both at ambient temperature and at cryogenic
temperature (2K). Their power handling and thermal properties will be
measured. The cavities and power couplers will be integrated into a prototype
cryomodule. The cryomodule will be tested and characterized with RF under
cryogenic conditions required for a high-power proton linac. This paper
describes the status of this program.
* Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
** Scientist from CEA/Saclay, France
Classification Category: T06
TH4098
Analysis of Performance Limitations for Superconducting
Cavities*
J.R. DELAYEN, C.E. REECE, L. DOOLITTLE, TJNAF
The performance of superconducting cavities in accelerators can be limited
by several factors, such as: field emission, quenches, arcing, rf power; and
the maximum gradient at which a cavity can operate will be determined by the
lowest of these limitation for that particular cavity. The CEBAF accelerator
operates with over 300 cavities and, for each of them, we have determined the
maximum operating gradient and its limiting factor. We have developed a model
that allows us to determine the distribution of gradients that could be
achieved for each of these limitations independently of the others. The
result of this analysis can guide an R&D program to achieve the best
overall performance improvement. The same model can be used to relate the
performance of single-cell and multi-cell cavities.
* Work supported by the U.S. DOE Contract # DE-AC05-84ER40150.
Classification Category: T06
TH4099
Resonance Control Cooling System for the APT/LEDA RFQ
R. FLOERSCH, G. DOMER, AlliedSignal
Cooling System layout is described as well as its operation to achieve the
desired inlet temperatures in each of the four RFQ segments. Use of flow
regulating valves to achieve uniform flow distribution to the 300 plus
channels is discussed which also enables use of centrifugal pumps. Control
system schema is described to regulate resonance frequency during steady state
operation.
Classification Category: T08
TH4100
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4101
First Tests of a Traveling-Wave Chopper for the ATLAS Positive Ion
Linac*
R.C. PARDO, J.M. BOGATY, B.E. CLIFFT, ANL
A ten segment traveling-wave chopper has been constructed and successfully
tested at 5% of the design 12 MHz repetition rate. The chopper must remove
unbunched tails from a partially bunched heavy-ion beam in order to avoid
undue emittance growth in the linac and the production of undesirable
satellite beam bunches. When poorly bunched beams travserse a chopper, the
traditional sine-wave chopper produces unacceptable transverse emittance
growth and unnecessary beam loss. Emittance growth and unnecessary beam losses
are expected to be much reduced in the traveling wave chopper. These first
tests have confirmed the validity of these claims, clearly showing much
reduced transverse emittance growth as compared to the original sine-wave
chopper and excellent selectivity for the desired beam. Details of these
tests will be presented and compared to calculations. Operation of the new
chopper at the full 12 MHz rate is the next goal. Development of a driver
power supply capable of full CW operation will also be described.
* This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Nuclear Physics
Division, under contract W-31-109-ENG-38.
Classification Category: T08
TH4102
Electrostatic Beam Kicker in the LEUTL at the APS *
G. WALDSCHMIDT, Y. KANG, ANL
An electrostatic kicker that was recently installed in the Low-Energy
Undulator Test Line (LEUTL) of the Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National
Lab has been computer simulated. The electromagnetic simulation code MAFIA
was used to evaluate the field distribution and its uniformity. The kicker
features off center electrodes to accommodate a larger deflection angle. The
two rectangular electrode plates have dimension 10 cm x l cm and are separated
by 1 cm. Numerical simulations also evaluate the effects of the electrode
locations on transverse and field uniformity.
* Work supported by U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy
Sciences under Contract No. W-31-109-ENG-38.
Classification Category: T08
TH4103
Improved Temperature Regulation of APS Linac Rf Components*
R. DORTWEGT, S. PASKY, M. WHITE, ANL
The temperature of the high-power linac rf components is regulated by water
from individual closed-loop DI water systems. Temperature changes in the
S-band high-Q SLED cavities result in undesirable changes in the positron beam
energy, thus a temperature regulation better than ± 0.1 degree F is required.
Modifications to the closed-loop water systems have enabled us to achieve a
regulation of ± 0.05 degrees over long periods. Regulation philosophy and
equipment will be discussed, and numerical results will be presented.
* Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy
Sciences, under Contract No. W-31-109-ENG-38.
Classification Category: T08
TH4104 (oral
poster TH3010)
Development of a Fast Traveling-Wave Beam Chopper for
the SNS Project*
S.S. KURENNOY, J.F. POWER, LANL
High current and severe restrictions on beam losses, below 1 nA/m, in the
designed linac for the Spallation Neutron Source (SNS) require clean and fast
- with the rise time from 2% to 98% less than 2.5 ns - beam chopping in its
front end, at the beam energy 2.5 MeV. The development of new traveling-wave
deflecting current structures, based on meander lines, is discussed.
Three-dimensional time-domain computer simulations are used to study transient
effects in the chopper and to optimize current structure design. Two options
for the fast pulsed voltage generator - based on FETs and vacuum tubes - are
considered, and their advantages and shortcomings for the case of the SNS
chopper are discussed.
*Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T08
TH4105
Experimental Results of the Active Deflection of a Beam from a Kicker
System*
Y. J. CHEN, G. CAPORASO, J. WEIR, LLNL
A high current kicker has been designed and tested on the ETA-II beam line.
A bias dipole which surrounds the kicker acts to deflect the beam in the DC
mode. High voltage pulsers (10kV) with fast rise times (~10ns.) are connected
to the internal striplines of the kicker. They are used to manipulate beams
dynamically. Camera photos which show the switching of the beam from one
position to another will be presented. Beam bug measurements of beam-induced
as well as active steering will be shown. These will be compared with
theoretical predictions [1].
*This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of
Energy by the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract No.
W-7405-Eng-48.
[1] G. Caporaso et al., Transmission Line Model of Stripline Kicker for Kiloamp
Continuous Beams, this conference.
Classification Category: T08
TH4106 (oral
poster TH3011)
Characterization of a Variable Energy Deuteron RFQ
System for Neutron Production
R.W. HAMM, AccSys Technology; B.R. KALA, U.A.S. TAPPER, J. GUZEK,
Schonland
Research Centre; C.B. FRANKLYN, Atomic Energy Corp. of South Africa
A compact dual energy radio-frequency quadrupole (RFQ) linac system, the
LANSARTM Model DL-5 manufactured by AccSys Technology, Inc., is
being
employed as a fast neutron source for a radiographic facility in South Africa.
This RFQ accelerator was designed to allow the acceleration of deuterium ions
to either of two selected energies, 3.90 or 4.86 MeV, for injection into a
high pressure windowless gas target that employs a rotating shutter. Precise
deuteron beam energies are required for effective use of this neutron
radiographic imaging technique. The beam size at the gas target must also be
small because it determines the spatial resolution of the imaging system. The
energy variation was accomplished by coupling two RFQ cavities with an
adjustable rf power phase shift in the second one to provide two modes of
operation, i.e. beam acceleration or beam transport. The beam dynamics code
PARMULT was used to design this RFQ system and calculate the linac output beam
parameters as a function of the phase shift between the two RFQ structures.
Experimental measurements have been made on the output beam using a Rutherford
back-scattering (RBS) technique and beam scanner developed for this system. In
this paper we will describe the results of the RBS energy and beam size
measurements, as well as their correlation with the design calculations.
Classification Category: U01
TH4107
Contribution withdrawn.
TH4108 (oral
poster TH3012)
Status of the INFN High Current SC Proton Linac for
Waste Transmutation
C. PAGANI, G. BELLOMO, INFN-Milano-LASA; R. PARODI, INFN-Genova; P.
PIERINI, INFN-Milano-LASA
INFN, jointly with ENEA, is working at the design study for an accelerator
driven waste transmutation subcritical system, TRASCO. In particular, our
group is studying the high energy section, above 100 MeV, of the high power
(> 30 MW) proton linac driver at 350 MHz, following the guidelines we
presented at the Linac'96 Conference. The funded activities include the
overall conceptual design of the three section SC linac and the development
and tests of prototypes for the cavities and cryomodules. An overview of the
status and perspectives of these activities will be given in this paper.
Classification Category: U03
TH4109
Characterization of High Power CW Klystrons and
Its Application to Low Level RF Control
A. ROHLEV, D. REESE, LANL
The power gain, phase delay, and line harmonic spectrum of a 1.3 MW, 350 MHz,
CW klystron amplifier have been measured as a function of input power. These
measurements along with the frequency response of the klystron were taken at
several constant perveance and constant impedance operating points. These
results are used to enhance the performance of the low level RF control system.
Classification Category: T03
 30 from 2keV/u to 150keV/u in cw
mode. When
completed the RFQ will comprise 19 modules, each composed of one split-ring
connected to 40cm of electrodes in quadrature for a total length of about 8m.
The first 7-ring portion of the RFQ is scheduled for testing with beam in an
interim configuration in early summer of this year. A copper wall internal to
the RFQ tank isolates the rf power to the electrode region. Electrostatic
quadrupoles are installed in the remainder of the tank to transport the beam
to a downstream diagnostic station. An injector composed of a 2.45GHz ion
source in a CUSP geometry and an electrostatic LEBT and matching section
delivers stable light ions to the RFQ. The beam is pre-bunched with an 11.7MHz
pseudo saw-tooth waveform across a single gap to satisfy an experimental
requirement for 90ns between beam bursts. The diagnostic station consists of
Faraday cups, a fast Faraday cup, an emittance rig, and an analyzing magnet.
The complete test set-up will be described and the results of commissioning
the injector and testing the RFQ will be summarized.
30 from 2keV/u to 150keV/u in cw
mode. When
completed the RFQ will comprise 19 modules, each composed of one split-ring
connected to 40cm of electrodes in quadrature for a total length of about 8m.
The first 7-ring portion of the RFQ is scheduled for testing with beam in an
interim configuration in early summer of this year. A copper wall internal to
the RFQ tank isolates the rf power to the electrode region. Electrostatic
quadrupoles are installed in the remainder of the tank to transport the beam
to a downstream diagnostic station. An injector composed of a 2.45GHz ion
source in a CUSP geometry and an electrostatic LEBT and matching section
delivers stable light ions to the RFQ. The beam is pre-bunched with an 11.7MHz
pseudo saw-tooth waveform across a single gap to satisfy an experimental
requirement for 90ns between beam bursts. The diagnostic station consists of
Faraday cups, a fast Faraday cup, an emittance rig, and an analyzing magnet.
The complete test set-up will be described and the results of commissioning
the injector and testing the RFQ will be summarized. .mm.mrad and
a very high
reliability. In order to match this beam into the Radio Frequency Quadrupole
linac (RFQ), its characteristics have to be monitored on-line. An emittance
measurement unit (EMU) located close to the RFQ entrance is a very powerful
diagnostic tool. We developed a non-interceptive EMU based on the video
analysis of the residual gas illumination. Methods and results are presented
and discussed.
.mm.mrad and
a very high
reliability. In order to match this beam into the Radio Frequency Quadrupole
linac (RFQ), its characteristics have to be monitored on-line. An emittance
measurement unit (EMU) located close to the RFQ entrance is a very powerful
diagnostic tool. We developed a non-interceptive EMU based on the video
analysis of the residual gas illumination. Methods and results are presented
and discussed.