TU4001
Upgrading of the Linear Induction Accelerator X-ray Facility
(LIAXF)
J. DENG, B. DING, J. SHI, Y. HE, J. LI, Q. LI, G. CAO, L. WEN, G.
DAI,
Institute of Fluid Physics
Linear Induction Accelerator X-ray Facility(LIAXF) is a pulsed X-ray
radiographic machine at Institute of Fluid Physics which produces X-ray by
impacting an electron beam on target with beam parameters of 10MeV, 2kA with
90 ns pulse width (FWHM). The machine was upgrated to LIAXMU by increasing
beam energy and current and reducing its spot size in 1996 in order to
increase the capability of penetration. Desciption and schematic of the LIAXFU
are presented. Simulation on the redesigned focusing section is also given.
Experimental results of 12meV, 2.6kA with 90 ns pulse width, about 4mm spot
size have been obtained.
Classification Category: A01
TU4002
Installation of the AIRIX Induction Accelerator
E. MERLE, CEA/PEM; P. ANTHOUARD, J. BARDY, CEA/Cesta; R. BOIVINET,
CEA/PEM; C. BONNAFOND, CEA/Cesta; M.A.
DARIZCUREN, J. DELVAUX, CEA/PEM; A. DEVIN, P. EYL, J. DE MASCUREAU, CEA/Cesta;
M.
MOUILLET,
J.C. PICON, O. PIERRET, CEA/PEM; A. ROQUES, C. VERMARE, D. VILLATE,
CEA/Cesta
AIRIX flash X-Ray Radiographic facility will consist of a 3.5kA/4.0MeV/60ns
injector and 64 induction cells powered by 32 H.V. generator (250 kV per
cell). Induction cells studies made on the PIVAIR accelerator [1], which is a
prototype of AIRIX, have allowed to design specific vacuum technology cells
(ferrite are under vacuum). In this paper, we will present the performances
of the injector, and particularly the time-resolved energy measurement, the
pepper-pot emittance measurement and the result of the three gradient method
experiment which has been made by optical transition radiation and Cerenkov
radiation observation. In a second part we will present the design of the
induction cells and their HV performances. We will see also the different
tests and characterization we make on each cell, and how we install the
accelerator. Finally, we will expose the intermediate experiment we plan to
do on the electron beam, after the first 16 cell, that are just installed.
Those experiment that will be a comparison between PIVAIR and AIRIX, will
permit to characterize the electron beam, and to optimize beam transport and
beam centering procedure, before continuing the installation.
[1] Ph. Eyharts et al. - Proceedings of PAC'97.
Classification Category: A01
TU4003
Experimental Results of Electron Beam Neutralization
Induced by a Limited Space-Charge Emission
C. VERMARE, J. LABROUCHE, P. LE TAILLANDIER, D. VILLATE,
CEA/Cesta
At the exit of the flash X-ray photography accelerator AIRIX, an intense
relativistic electron beam (4kA, 16-20MeV, pulse length=80ns) impinges on a
high Z substance. The quality of the radiography obtained is directly tied to
the properties of the electron beam. In a preliminary study (LELIA linac,
1-2MeV, 1kA) of the optical diagnostics (Cerenkov effect with a
SiO2 target) needed to measure the beam size, a very strong
perturbative effect was observed. The size of the focal spot was observed to
vary with time during the beam pulse. This observation was confirmed on last
OTR studies with the PIVAIR induction linac (8MeV, 4kA, pulse length=80ns).
After analysis of these experimental results, an explanation of the effect in
terms of the emission of positive ions by the target, and their subsequent
tendency to move upstream have been confirmed by "PIC" simulations. An
additional measurement of the flux of emitted ions has also been performed.
Classification A01
TU4004
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4005
Design of a Sub-Picosecond, High Charge Electron
Linac*
H. BLUEM, C. PAULSON, M. REUSCH, A. TODD, Northrop Grumman Corp.
A photocathode-based electron linear accelerator, and associated transport
line, which is capable of delivering sub-picosecond electron pulses of up to 3
nC has been designed. The gun is 2.5 cells with a magnesium photocathode,
followed by a four cell booster accelerator. These are designed to produce an
electron bunch at a nominal energy of 15 MeV with a longitudinal phase space
which is optimized for magnetic compression inside a 90 degree achromatic
bend. The predicted performance of this beamline (obtained through PIC
simulations and a nonlinear beam transport code) is a charge of > 2 nC in a
pulse width of < 0.7 ps. This same linac beamline is also designed to
deliver in excess of 90 nC in somewhat longer pulses. We will present the
results of our simulations and the detailed design of this linac and transport
system.
*This work was supported by Argonne National Laboratory under contract #
972582401.
Classification Category: A01
TU4006
Development of an Upgrade of the CEBAF Acceleration System*
J.R. DELAYEN, TJNAF
Long-term plans for CEBAF at Jefferson Lab call for achieving 12 GeV in the
middle of the next decade and 24 GeV after 2010. Such energies can be
achieved within the existing footprint by fully populating the accelerator
with cryomodules capable of providing 3 to 4 times as much voltage as the
design value of the existing within the same length. In particular, this
requires for the development superconducting cavities capable of operating at
gradients above 12 MV/m and Q close to 1010. An R&D program for
the development of the cryomodules is under way and will be presented, as well
as various options for the upgrade path.
* Work supported by the U.S. DOE Contract # DE-AC05-84ER40150
Classification Category: A01
TU4007
Latest Developments from the S-DALINAC and its Free- Electron- Laser
*
M. BRUNKEN, S. DÖBERT, R. EICHHORN, H. GENZ, H.-D. GRÄF,
T.
HAMPEL, S. KOSTIAL, U. LAIER, H. LOOS, A. RICHTER, B. SCHWEIZER, A. STASCHECK,
O. TITZE, T. WESP, Institute für Kernphysik Tu-Darmstadt
The FEL at the superconducting electron accelerator S-DALINAC has been
operated at wavelengths between 6.6 and 7.8 µm corresponding to electron beam
energies between 31.5 and 29.6 MeV respectively. In house developments like
active stabilization of the optical cavity's length based on a laser
interferometer and a fast 10 channel on-line-spectrometer for the near
infrared laser radiation were incorporated and used for investigation of the
properties of the FEL itself. In addition a simple focusing system produced
power densities of 108 W/cm2 and enables us to perform
first ablation experiments from different tissues. To optimize the complicated
bunching process, the low energy part of the S-DALINAC was carefully studied
by tracking calculations in order to achieve bunch lengths < 3 ps
corresponding to peak currents > 1.5 A, necessary to operate the FEL
reliably in the saturated regime. For operation at higher energies using two
recirculations of the electron beam, longitudinal tracking simulations show
that off crest acceleration together with nonisochronous recirculation
introduce longitudinal stability resulting in significant improvement in
energy spread. As some of the sc cavities showed Q degradation due to organic
contamination, eight cavities were cleaned by a method involving organic
solvents and buffered chemical polishing. During the same shutdown the beam
transport to the experimental areas was redesigned maximizing its acceptance
and rebuilt.
* Supported by BMBF under contract number 06 DA 820 and by DFG under
contract number RI 242/12-1.
Classification Category: A01
TU4008
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4009
1GeV Linac at Fermilab*
M.B. POPOVIC, A. MORETTI, C.W. SCHMIDT, R. NOBLE, FNAL
A proposed linac injector for a new proton source complex at Fermilab is
assumed to have a kinetic energy of 1 GeV. This linac would be sized to
accelerate ~100 mA of H- beam in a ~200 microsecond pulse at a 15 Hz
repetition rate. This would be adequate to produce ~1.0E14 protons per pulse
allowing for future increases in antiproton neutrino prodution as well as
providing a source for a possible muon collider. An alternate proposal is to
add 600 MeV of side coupled cavity linac at 805 MHz to the existing 400 MeV
Linac. This addition may either be in a new location or use the present
Booster tunnel. A discussion of these possibilities will be given.
*Work supported by the U.S. Dept. of Energy under contract No.
DE-AC02-76CH03000.
Classification Category: A02
TU4010
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4011 (oral
poster TU3001)
Design of the 200-MeV Proton Linac for the Japan Hadron
Facility
T. KATO, Y. YAMAZAKI, KEK
A 200-MeV proton linear accelerator for the JHF has been designed. A peak
current of 30 mA with 500 micro-sec pulse duration will be accelerated at a
repetition rate of 25 Hz. The linac consists of a 3-MeV radio-frequency
quadrupole linac (RFQ), a beam-transport line from the RFQ to the DTL (MEBT),
a 50-MeV drift tube linac (DTL) and a 200-MeV separated-type drift tube linac
(SDTL). A frequency of 324 MHz has been chosen for all of the rf structures. A
future upgrade plan of up to 400 MeV is also considered, in which
annular-coupled structures (ACS) of 972 MHz will be used in an energy range
of above 150 or 200 MeV. There are three distinct features in the design. The
first is stable operation with high performance for a beam-loss problem. The
second is a total high shunt impedance, achieved by adopting the SDTL
structure. The third is the adoption of klystrons of 2.5-MW peak output power
rather than conventional 200-MHz triodes. The details of the design,
including the results of beam simulation studies using two kinds of focusing
methods (equipartitioning focusing and constant phase-advance focusing in
transverse motion) are presented.
Classification Category: A02
TU4012
Development of a Commissioning Plan for the APT Linac*
L. W. FUNK, WSRC; K. R. CRANDALL, Techsource; J. D. GILPATRICK, E.
R.
GRAY,
L. J. RYBARCYK, T. P. WANGLER, LANL
The APT proton linac will have an average beam power of 170 MW, which
exceeds by two orders of magnitude that of the next largest proton linac.
Safe, successful and prompt commissioning of this accelerator will be the
culmination of a years-long series of activities which will include: ensuring
that the design incorporates those features necessary for a successful
demonstration of technical performance; a careful and tightly integrated
program of subsystem acceptance testing and installation; thorough planning to
ensure the timely availability of infrastructure, resources and trained staff;
and a comprehensive test plan. All of these activities require as a starting
point a complete identification of all performance characteristics that must
be measured to confirm that the linac meets its design objectives. This paper
will present our present understanding of the technical objectives of the
commissioning program, review the impact of that understanding on the design
of the accelerator, and summarize the issues which remain to be addressed and
the plan to address them.
* Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy
Classification Category: A02
TU4013 (oral
poster TU3002)
A Linac for the Spallation Neutron Source*
A. J. JASON and the SNS LINAC Design Team, LANL
The Spallation Neutron Source Project (SNS) accelerates H- ions to
an
energy of 1.0 GeV with an average current of 1-mA for injection in an
accumulator ring that produces the short intense burst of protons needed for
the spallation-neutron source. The linac will be the most intense source of
H- ions and as such requires advanced design techniques to meet
project
technical goals as well as to minimize cost. In particular, low beam loss is
stressed for the chopped beam, placing strong requirements on the beam
dynamics and linac construction. Additionally, the linac is to be upgraded to
the 2- and 4-MW beam-power levels with no increase in duty factor. We give an
overview of the linac design parameters and discuss the special challenges and
status of the effort.
* Work supported by the Office of Energy Research, Basic Energy Sciences,
of the US Department of Energy; and the Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
Classification Category: A02
TU4014
Status Update on the Low-Energy Demonstration
Accelerator (LEDA)*
H. V. SMITH, JR., J. D. SCHNEIDER, LANL
As part of the linac design for the accelerator production of tritium (APT)
project, we are assembling the first 10-MeV portion of this cw, 100-mA proton
accelerator. The primary objective of this low-energy demonstration
accelerator (LEDA) is to verify the design codes, gain fabrication knowledge,
understand beam operation, and improve prediction of costs and operational
availability for the full 1000- to 1700-MeV APT accelerator. This paper
provides an update on this past year's progress that includes extensive beam
tests of the LEDA injector using the Chalk River Injector Test Stand (CRITS)
radio-frequency quadrupole (RFQ) accelerator, which results in production of a
cw, 100-mA, 1.25-MeV RFQ output beam; fabrication, assembly, tuning, and
installation of the 6.7-MeV LEDA RFQ; upgrades to the facility; installation
and testing of the 350-MHz RF system; installation of the HEBT; and
installation (as well as prototype testing) of the LEDA ogive beam stop.
First tests with the 6.7-MeV, 100-mA, cw beam from the RFQ are scheduled for
late fall. References will be given to many detailed papers on LEDA at this
conference.
* Work supported by the US DOE, Defense Programs.
Classification Category: A02
TU4015
Beam Dynamics Design of the 211 MEV APT Normal Conducting
LINAC*
L. M. YOUNG, J. H. BILLEN, H. TAKEDA, R. L. WOOD, LANL
This paper presents the design of the 6.7 to 211 MeV Normal Conducting
Linac for the Accelerator for Production of Tritium (APT) project. This linac
was designed with the new version of the PARMILA [1]. This linac accepts the
beam from the 6.7 MeV radio frequency quadrupole without a separate matching
section. At about 10 MeV, it has a smooth transition in the length of period
from 8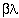 to 9
to 9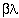 in quadrupole focusing lattice. This adjustment of
the period was needed to provide sufficient space for the quadrupole focusing
magnets and beam diagnostic equipment. The linac consists of the coupled
cavity drift tube linac [2] up to 100 MeV and coupled cavity linac above 100
MeV.
in quadrupole focusing lattice. This adjustment of
the period was needed to provide sufficient space for the quadrupole focusing
magnets and beam diagnostic equipment. The linac consists of the coupled
cavity drift tube linac [2] up to 100 MeV and coupled cavity linac above 100
MeV.
*Work supported by the U. S. Department of Energy.
[1] H. Takeda, J. H. Billen, "Recent Developments in the Accelerator
Design Code PARMILA," this conference.
[2] J. H. Billen, et al., "A New RF Structure for Intermediate-Velocity
Particles," Proc. of the 1994 Linear Accelerator Conference, August
21-26, 1994, Tsukuba, Japan.
Classification Category: A02
TU4016 (oral
poster TU3003)
First Results of the Two-Beam Funneling
Experiment*
A. FIRJAHN-ANDERSCH, A. SCHEMPP, J. THIBUS, E. WINSCHUH, H. ZIMMERMANN,
IAP-Univ. of Frankfurt
High intensity accelerator concepts for Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion
(HIIF) injectors require small emittance, high current and high energy beams.
The improvement of brightness in such a driver linac is done by several
funneling stages at low energies, in which two identically bunched ion beams
are combined into a single beam with twice the frequency, current and
brightness. For the Heavy-Ion Driven Ignition Facility (HIDIF) we have
proposed the use of an two-beam accelerator structure which provides two beams
within one cavity and a single r.f. deflector structure which bends the two
beams to one common axis. The progress of the experiment and first beam-test
results will be
presented.
* This work is supported by the BMBF
Classification Category: A02
TU4017 (oral
poster TU3004)
Present Performance of the CERN Proton
Linac
C.E. HILL, A. LOMBARDI, E. TANKE, M. VRETENAR, CERN
The original 1973 design specification of the CERN 50 MeV Proton Linac was
for a 150 mA beam but this intensity was rarely used. Preliminary tests for
the high brightness beam required for LHC indicated that 170 mA could be
produced for short pulses (30 µs). Since then further optimisation has enabled
the 170 mA to be delivered reliably, within the nominal emittances and
dispersion, in long pulses (120 µs) to the user (PS Booster, about 80 m
downstream of the linac). The improvements will be described along with the
steps envisaged to attain a goal of more than 180 mA.
Classificaiton Category: A05
TU4018
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4019
Fermilab Linac Operations, Studies and Improvements*
L.J. ALLEN, C.W. SCHMIDT, M.B. POPOVIC, FNAL
The Fermilab Linac operated as an injector for the Tevatron Fixed Target
Program, Booster studies and for neutron production for cancer treatment
during 1997 and 1998. Operational reliability was 98% of the scheduled
operating time. The beam current was generally in the 45 to 48 mA range. After
completion of the Fixed Target Program, the Linac embarked on a series of
studies. The studies were intended to verify visual survey data indicating a
misalignment of the low energy linac, correct the misalignment, and check the
linac RF phase and amplitude settings. Operations data and studies results
will be presented.
*Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy under contract No.
DE-AC02-76CH03000.
Classification Category: A05
TU4020
Moscow Meson Factory Linac - Operation and
Improvements
S. K. ESIN, L. V. KRAVCHUK, P. N. OSTROUMOV, V. L. SEROV, INR
RAS
During 1997-1998 the Moscow Meson Factory Linac (MMFL) provided 3800 beam
hours for experiments, isotope production, and systems reliability upgrades.
The new beam diagnostics computer controls exert a very important impact on
the beam quality and operational efficiency of the linac. A crucial
experiment was conducted that revealed the cause of the discrepancy between
the calculated and the measured capture efficiency. A safe triple protection
circuit was introduced after a hole was accidently burned in the isotope
production channel beam pipe. A new injection scheme implementation is
underway which must increase the average beam current from the recent 70 mcA
to about 200 mcA. During the March 1998 shift the MMFL worked for the Pulsed
Neutron Source for the first time.
Classification Category: A05
TU4021
Status of a New Switchyard Design for LANSCE*
R. W. GARNETT, E. BJORKLUND, M. BORDEN, C. ROSE, F. SHELLEY, J. D.
ZUMBRO, LANL
The details of a new design for a section of the LANSCE 800 MeV beam
switchyard will be discussed. At present, the switchyard is used to deliver a
proton beam to experimental Area-A and an H--ion beam down Line-D.
The total H- repetition rate is 120 Hz. Of that 120 Hz, 100 Hz is
transported to the Weapons Neutron Research (WNR) area. The remaining 20 Hz is
injected into the Proton Storage Ring (PSR). In order to provide H-
beam to other experimental areas without interfering with the PSR operations,
a new design of the switchyard was completed. The new design incorporates the
use of pulsed kicker magnets to deflect a fraction of the H- beam,
normally delivered to the WNR area, down Line-C at the demand of the
experimenters.
*Work supported by the U. S. Department of Energy Contract
W-7405-ENG-36.
Classification Category: A05
TU4022
Understanding Accelerator Reliability
C. PIASZCZYK, Northrop Grumman Corp.
Over the period of several years, the author studied reliability of both
planned and existing accelerator systems. This involved collection and
analysis of data gathered at various operating accelerator facilities and
mathematical modeling of accelerator design concepts. Although the surveyed
accelerator facilities are complex and different in details, they all share
common operational characteristics. Moreover, they typically consist of
just a few typical components: ion sources, focusing magnets, magnet power
supplies, RF windows, circulators, rf amplifiers, high voltage components,
etc. It should be therefore possible to use the accumulated operational
experience to optimize the envisioned future concepts and to extend the
operating performance of existing machines. In the process, accelerators can
serve as a testbed for developing an understanding of the reliability of
repairable systems.
Classification Category: A05
TU4023
Status of 200 MeV Electron LINAC and Its
Applications
Y.J. PEI, Y.F. WANG, S. DONG, X.F. LUO, G.R. HUANG, G.C. WANG, W.
WANG,
Y.X. LI, University of Science & Technology of China
The 200 MeV Electron LINAC is an injector of Electron Storage Ring which
was the first dedicated synchrotron Radiation facility in China. The LINAC has
been running well for ten years, since 1987. Typical operation parameters are
energy of 200 MeV, current of 50 mA and energy spread of 0.8%. Some
improvements are described in this paper, such as developing an energy
stabilized system, adding a post-transport line in order to guide the beam
into a nuclear physics experimental hall, developing a two mode combined
pulser for the electron gun to meet single-bunch and multi-bunch mode running
in the storage ring. Some applications are briefly described here also. Some
research results are given, such as isotopes products: 123I, 11C, 15O, 18F
etc.
Classification Category: A05
TU4024
Status of PLS 2 GeV Electron Linac Performance*
M.H. CHO, K.R. KIM, J.S. OH, S.H. PARK, S.S. PARK, I.S. KO, W.
NAMKUNG,
PAL-POSTECH
The 2 GeV electron linac at the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL) has
been operated continuously as a full energy injector for the Pohang Light
Source (PLS) since its completion on Dec. 7, 1994. There has been continuous
effort to make the linac system more stable and reliable, such as the
modifications of the klystron modulators, temperature stabilization of the
main rf drive line, installation of one more klystron-modulator station with
the addition of two sets of acceleration sections. The average high voltage
operation time of the klystrons (E-3712, Toshiba) installed at the very
beginning (8 tubes are survived out of total 11 tubes) has reached near
32,000 hours as of May 1998. Current overall system availability is over 90%.
In this paper, we report the major linac system upgrade for the nominal 2.5
GeV operation as well as the system performance and relevant machine
statistics such as lifetime of klystrons and thyratrons, and overall system's
availability, and others.
* Work supported by POSCO and MOST, Korea.
Classification Category: A05
TU4025 (oral
poster TU3005)
Achieving 800kW CW Beam Power and Continuing Energy
Improvements in
CEBAF*
C.E. REECE, TJNAF
During the past year, CEBAF at Jefferson Lab has demonstrated its full
capacity of sustained 800 kW beam power. All systems performed as intended.
The energy stability at the design parameters of 4.0 GeV, 200 microamps CW
beam was measured to be better than 3E-5 rms. During the Fall of 1997, physics
experiments were conducted using 4.4 GeV beam. Having demonstrated the
benefits of in situ helium/rf processing of SRF cavities for increasing the
energy reach of CEBAF, a program of processing all installed cryomodules has
begun. This processing has proven effective against the principal chief
gradient limitation of the SRF cavities in CEBAF: discharges at the cold rf
waveguide window, induced by electron field emission in the cavities.
Approximately half of the cavities are limited by such effects. Sustained
operation above 5.0 GeV has been scheduled, and we are preparing for physics
runs above 5.5 GeV. Successes and difficulties encountered on this upgrade
path will be presented.
*Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, contract
DE-AC05-84ER40150.
Classification Category: A05
TU4026
Stability of the CLIC Drive Beam Accelerator
D. SCHULTE, CERN
(R. Ruth, presenter)
The drive beam of the Compact Linear Collider (CLIC) needs to have a
current of several amperes. The time structure of this beam is discussed.
First results on longitudinal single bunch effects are presented and
achievable bunch lengths and sensitivity to jitter of the gradient, initial
energy and charge are analysed. The transverse stability of the beam is
discussed based on the present cavity model. The requirements on the damping
and detuning of the cavities are detailed. A beam-based alignment technique is
presented and the stability with respect to jitter and ground motion is
investigated.
Classification Category: D01
TU4027
High Current Transport and Acceleration at the Upgraded UNILAC
W. BARTH, J. GLATZ, J. KLABUNDE, GSI Darmstadt
The UNILAC will be upgraded as a high current injector for SIS. The
Wideroe section will be replaced by an RFQ-IH-type accelerator. This paper
focuses on beam dynamics studies in the stripper section, the poststripper
Alvarez accelerator and the beam transport line to SIS including a second
stripper section. The beam dynamics investigations are faced with
considerable space charge effects along the UNILAC. Most severe space charge
forces occur after the charge state jump in the gas stripper at 1.4 MeV/u. A
new design of the charge separation system will be presented. Furthermore,
simulation results for matching to the Alvarez linac, emittance growth effects
in the poststripper linac, equipartitioning and longitudinal mismatching will
be discussed. The beam transfer to SIS will include a modified foil stripper
and charge separation system, the beam brilliance loss due to foil straggling
and space charge forces will be calculated. Beam experiments at the present
UNILAC with high current beams supported the design studies, experimental
results will be reported.
Classification Category: D01
TU4028
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4029
Analysis and Modeling of a Stripline Beam Kicker and
Septum*
B.R. POOLE, G.J. CAPORASO, Y. J. CHEN, LLNL
A fast stripline beam kicker and septum are used to dynamically switch a
high current electron beam between two beam lines. The transport of the beam
through these structures is determined by the quality of the applied
electromagnetic fields as well as temporal beam induced effects due to the
wakefields produced by the beam. In addition, nonlinear forces in the
structure will lead to emittance growth. The effect of these issues is
investigated analytically and by using particle transport codes. Due to the
distributed nature of the beam-induced effects, multiple macro-particles
(slices) are used in the particle transport code, where each slice consists of
an ensemble of particles with an initial distribution in phase space. Changes
in the multipole moments of an individual slice establish electromagnetic
wakes in the structure and are allowed to interact with subsequent beam
macro-particles to determine the variation of the steering, focusing and
emittance growth during the beam pulse.
*This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of
Energy by the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under contract No.
W-7405-Eng-48
Classification Category: D01
TU4030
Higher-Order-Modes and Beam Breakup Simulations in the Jefferson Lab
FEL Recirculating Linac*
L. MERMINGA, I. CAMPISI, TJNAF
The Jefferson Lab FEL driver accelerator is a recirculating,
energy-recovering superconducting linac designed to attain a CW beam current
of 5 mA. Measurements of the external Q's of the TE111 and
TM110 dipole passbands of all 10 superconducting cavities yield
values much higher than anticipated for some of the TE111
resonances. These enhanced Q's are related to strong polarization of the modes
along and orthogonal to the fundamental power coupler. The reasons of such
polarization will be discussed together with solution for this potentially
harmful problem. Threshold currents for the multipass beam breakup (BBU)
instability were calculated to evaluate the safety margin available in the
operation of the accelerator. TDBBU simulations were done with measured HOM
parameters and the threshold current was determined to be 27 mA. The dominant
contribution to the instability comes from a few high Q resonances of the
y-polarization of the 4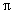 /5 TE111 mode. If these
modes were
adequately damped--which might be possible in the future with minor hardware
changes--then simulations predict that the threshold current would increase by
almost an order of magnitude. The results of these measurements and
simulations, as well as an analytical treatment of the BBU during energy
recovery, are presented.
/5 TE111 mode. If these
modes were
adequately damped--which might be possible in the future with minor hardware
changes--then simulations predict that the threshold current would increase by
almost an order of magnitude. The results of these measurements and
simulations, as well as an analytical treatment of the BBU during energy
recovery, are presented.
* Work supported by the U.S. DOE Contract # DE-AC05-84ER40150.
Classification Category: D01
TU4031
TESLA Injektor Simulations with MAFIA
P. SCHUETT*, T. WEILAND, TU-Darmstadt
The TESLA Test Facility (TTF) is a test bed for the superconducting option
of a linear e+/e- collider in the TeV regime. The
injector delivers a 20 MeV beam with 8 nC charge per bunch of 1 mm length. It
consists of an RF-gun, a superconducting 9-cell Capture Cavity and a chicane
bunch compressor. The MAFIA modules TS2 and TS3, the particle in cell programs
in 2D and 3D, as well as the module L, a tracking program, have been used to
study the particle dynamics in the TTF, e.g. the emittance growth due to space
charge effects in the bunch compressors. Dedicated interfaces for the three
different simulation tools allow to study components separately and to hand
over beam data from one accelerator section to another or one simulation tool
to another respectively.
* Work supported partly by DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft).
Classification Category: D01
TU4032
Halo Formation in 3-D Bunches with Different Phase
Space Distributions
A.V. FEDOTOV, R.L. GLUCKSTERN, Univ. of Maryland; S.S. KURENNOY,
R.D.
RYNE,
LANL
A realistic treatment of halo formation must take into account 3-D beam
bunches and 6-D phase space distributions. We recently constructed,
analytically and numerically, a new class of self-consistent 6-D phase space
stationary distributions, which allow us to study the halo development
mechanism without being obscured by the effect of beam redistribution. Now
that we have established the parameters which lead to halo formation in 3-D
beam bunches for the 6-D self-consistent phase space distribution, we explore
distributions which are not self-consistent, to determine the extent to which
the relatively rapid redistribution in the 6-D phase space contributes to the
formation of halos.
Classification Category: D01
TU4033
Study of the Transverse Beam Motion in the DARHT Phase II Accelerator*
Y.-J. CHEN, T. L. HOUCK, LLNL; W. M. FAWLEY, LBNL
The accelerator for the second-axis of the Dural Axis Radiographic
Hydrodynamic Test (DARHT) facility will accelerate a 4 kA, 3.5 MeV, 2 ms long
electron current pulse to 20 MeV. The energy variation of the beam within the
flat-top portion of the current pulse is ±
0.5%. The performance of the DARHT Phase II radiographic machine requires the
transverse beam motion to be much less than the beam spot size which is about
1.5 mm diameter on the x-ray converter. In general, the leading causes of the
transverse beam motion in an accelerator are the beam breakup instability and
the corkscrew motion. We have modeled the transverse beam motion in the DARHT
Phase II accelerator with various magnetic tunes and accelerator cell
configurations by using the BREAKUP code. The predicted sensitivity of
corkscrew motion and BBU growth to different tuning algorithms will be
presented.
* The work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of
Energy by LLNL under contract W-7405-ENG-48, and by LBNL under contract
AC03-76SF00098.
Classification Category: D01
TU4034 (oral
poster TU3006)
Controlling Backstreaming Ions from X-ray Converter
Targets with Time Varying Final Focusing Solenoidal Lens and Beam Energy
Variation*
Y.-J. CHEN, A. C. PAUL, LLNL
Performance of high resolution x-ray radiography facilities requires high
current electron beams to be focused to a millimeter spot size on an x-ray
converter throughout the entire current pulse. Within a single pulse, the
heating of the target by the electron beam will lead to rapid desorption of
surface contaminants. The space charge field of the electron beam will pull
ions out of this plasma layer into the beam. These backstreaming ions can form
an ion focusing channel and overfocus the electron beam. As the ions move
upstream in time, the net focusing strength increases. The final beam spot
size on the target would then change in time and typically be larger than
intended. We have studied the possibility of mantaining a constant final spot
size for the entire current pulse by using either a time varying final
focusing solenoidal field or beam energy variation to compensate the time
varying ion focusing effects. However, the required time varying rate for both
the solenoidal field and the energy variation are large. The predicted final
focusing with various beam parameters will be presented.
* The work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of
Energy by LLNL under contract W-7405-ENG-48.
Classification Category: D02
TU4035
EM-PIC Simulations of e-Beam Interaction with Field Emitted Ions from
Bremsstrahlung Targets *
P. W. RAMBO, S. BRANDON, LLNL
We investigate electron beam defocusing caused by field emitted ions from
the bremsstrahlung target of a radiography machine using fully electromagnetic
particle-in-cell simulations. This possibly deleterious effect is relevant to
both current radiography machines (FXR) and machines being planned (DARHT and
AHF). A simple theory of the acceleration of ions desorbed from the heated
target, and subsequent beam defocusing due to partial charge neutralization is
in reasonable agreement with the more detailed simulations. For parameters
corresponding to the FXR machine (I=2.3 kA, E=16 MeV), simulations assuming
space-charge-limited emission of protons predict prompt beam defocusing. Time
integrated spot-size measurement, however, is dominated by early-time small
spot brightness, and so is not a sensitive diagnostic. Comparisons are made to
available FXR data. We also investigate use of recessed target geometries to
mitigate field emitted ion acceleration; only modest improvements are
predicted.
* This work was performed under the auspices of the U. S. Department of
Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract No.
W-7405-Eng-48.
Classification Category: D02
TU4036
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4037
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4038
Model-Independent Analysis of Beam Dynamics*
J. IRWIN, C.X. WANG, Y. YAN, K. BANE, Y. CAI, F.J. DECKER, M. MINTY,
G.
STUPAKOV, SLAC
In this paper, we report a novel method to analyze the beam dynamics based
on BPM readings. This analysis is independent of any machine models. Instead,
it relies on the ensemble of readings from a large number of BPMs for a large
number of pulses. In addition, pulse-by-pulse information of beam parameters
and machine status are used. By taking advantage of the spatial correlation
and temporal structure of all these signals, our analysis allows observation
of beam dynamics at a level far beyond the single BPM resolution. Further
more, unexpected beam dynamics as well as machine information can be revealed.
Both simulation and experimental results from SLC will be presented.
*Work supported by the Department of Energy under Contract No.
DE-AC03-76SF00515
Classification Category: D02
TU4039
Multiple Coupling and Beam Loading of a RF Cavity
H. SAFA*, LANL and CEA/Saclay
Future high power accelerators are aiming at increasing the power
transferred to the beam through radiofrequency (RF) cavities. Consequently,
multiple main coupler drives may be required to withstand the high RF power
needed per cavity. An analysis including multiple couplers and beam loading is
described here, featuring the interaction between all couplers, the beam and
the cavity. In this description, the beam is shown to act as if it were
merely an additional drive for the cavity. Special focus is given to the case
of superconducting cavities in a continuous (CW) operation mode. Some
important conclusions derived from this analysis are briefly discussed as, for
example, power coupler fault conditions or a way to handle the commissioning
of an accelerator in a CW mode.
* Work performed while on assignment at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
Classification Category: D04
TU4040
Analytical Treatment of Single Bunch Stability in a
Linac
G. GUIGNARD, J. HAGEL, CERN
Single bunch stability is analysed by solving the equation of motion of the
particles travelling in a linac, for a Gaussian distribution of charge, a
linear variation of the transverse wakefield along the bunch, a smooth
focusing and negligible acceleration. The treatment is based on a non-standard
perturbation expansion that has been specifically developed for this study and
preserves at each order the intrinsic detuning likely to stabilise the
resonant break-up. It provides a closed expression for the tune shift along
the bunch resulting from BNS damping and autophasing, methods proposed in the
past to control the emittance, and a first order solution for the transverse
off-sets within the bunch. The analytic result obtained makes it possible to
study the behaviour of the solution and compute the emittance dilution in
specific cases. The present theory is a useful complement to the numerical
simulations done with the MUSTAFA code for the Compact LInear Collider scheme
(CLIC). It also gives an interesting as well as comprehensive view of the
physics involved in the single bunch motion and the damping of the
instability.
Classification Category: D04
TU4041
Application of the Mode-Matching Technique to the Analysis of
Waveguide Arrays
A. JOESTINGMEIER, M. DOHLUS, N. HOLTKAMP, DESY
In this contribution the mode-matching technique is applied to compute the
absorption characteristics of a two-dimensional array of rectangular
waveguides. This analysis is motivated by a proposal of a broadband absorber
for TESLA. Outside the waveguide array the so-called Rayleigh expansion is
used which represents the electromagnetic field in terms of space harmonics
whereas the complete modal spectrum of eigenmodes is taken into account inside
the waveguides. In the case of normal incidence the validity of the presented
method is confirmed by MAFIA computations. The absorption characteristics for
various angles of incidence are calculated for a broad frequency range. The
accuracy of the results is checked by a study of convergence. It is shown that
the Rayleigh expansion has to be modified if the waveguide array is excited by
an ultrarelativistic beam instead of an incoming plane wave. For an array of
parallel-plate waveguides numerical results (beam impedance, wakefield, loss
parameter) are presented and compared with those obtained by other
methods.
Classification Category: D04
TU4042
Simulation Study of the Bunching Section of Xband Klystrons
S. MATSUMOTO, S. MICHIZONO, H. TSUTSUI, Y.H. CHIN, S. FUKUDA,
KEK
A precise simulation of a klystron is useful to understand its operation
and preferable for its design work. For this purpose, MAGIC code, which is a
2.5 dimensional fully electromagnetic and relativistic PIC code for
self-consistent simulation of plasma physics problems, is used. Simulation
works for the production of the beam, the modulated beam motion and the
beam-cavity interaction at the output cavity as well as the gain cavities can
be done by this code. In this article, the simulation of the buncher section
of a relativistic klystron, such as KEK XB72K or SLAC XL-4, is reported. The
process of the modulation on the beam motion and the evolution of rf current
is observed.
Classification Category: D04
TU4043 (oral
poster TU3007)
Electron Gun Simulation Using MAGIC
S. MICHIZONO, H.TSUTSUI, S. MATSUMOTO, Y. H. CHIN, S. FUKUDA,
KEK
In a future linear collider such as Japan Linear Collider (JLC) and SLAC
NLC, high power klystrons at X-band (11.424 GHz) will be used. In these
klystrons, the beam (>350A) should be compressed to around the radius of 3
mm and the area-convergence ratio of the beam is more than 100. In such a high
beam intensity, the precise beam trajectory is analyzed by the suitable gun
simulation.
In this report, electron-gun regions of some klystrons (S- and X-band) are
simulated by MAGIC, which is the 2.5-D fully electromagnetic and relativistic
particle-in-cell (PIC) code for self-consistent simulation of plasma physics
problems. Simulation results indicate that the profile of the current density
is almost same to the EGUN and the perveance is larger than the EGUN predicted
value and almost same to the measured value. The particle data (including
momentum) from the electron gun are exported to the next rf interaction region
and the whole structure of the klystron can be simulated by MAGIC.
Classification Category: D04
TU4044
High Energy Beam Transport Beamline for LEDA*
W. LYSENKO, LANL; M. SCHULZE, General Atomics
This paper describes the High Energy Beam Transport (HEBT) beamline for the
Low Energy Demonstration Accelerator (LEDA), which is part of the Accelerator
Production of Tritium (APT) project. Space-charge effects are important in
this 6.7 MeV 100 mA CW beam. Simulations are presented showing that
maintaining strong focusing (no large magnet separations) and minimizing beam
size variations (avoiding rapid increases in the charge density) in the
upstream part of the beamline are important for avoiding halo formation. The
beamline design was obtained with the help of the TRACE 3-D design code and
the beamline properties were verified with different 2-D and 3-D
particle-in-cell (PIC) simulation codes. Comparisons show that 3-D effects
are important and that TRACE 3-D predicts rms beam properties well. The PIC
simulations are important for determining the presence of beam halo, which we
define as a long tail in the charge distribution. The PIC simulations make
clear predictions concerning the presence or absence of beam halo as a
function of the HEBT tune. HEBT experiments at LEDA are proposed to verify
the accuracy of the simulation codes' ability to predict halo.
*Work supported by the U.S. DOE, Defense Programs.
Classification Category: D04
TU4045
Beam Dynamics Simulation of the Spallation Neutron Source Linear
Accelerator *
H. TAKEDA, T. BHATIA, J. H. BILLEN, LANL
The accelerating structure for Spallation Neutron Source (SNS) consists of
a drift-tube linac (DTL) from 2.5 to 20 MeV, a coupled-cavity drift-tube linac
(CCDTL) to 96 MeV, followed by a conventional coupled-cavity linac (CCL) to 1
GeV. The CCDTL and CCL have regularly spaced drift lengths between segments of
accelerating structure for the quadrupole focusing magnets and diagnostics.
Across transitions between structure types we maintain continuous average
focusing strength per unit length, both transversely and longitudinally. We
discuss details of the transverse and longitudinal matching between the
402.5-MHz DTL and the 805-MHz CCDTL. We present end-to-end multiparticle
simulations of the beam emerging from the RFQ through the rest of the linac.
High cavity stored energy helps to reduce the amplitude of cavity field
variations caused by chopping the beam. We discuss the beam characteristics
along the linac at the design field level and at the peaks and valleys of the
field over a chopping period.
* This research is sponsored by the Division of Materials Sciences, DOE,
under contract DE-AC05-96OR22464 with Lockheed Martin Energy Research Corp
Classification Category: D04
TU4046
Using of LIDOS.RFQ Codes for CW RFQ Designing
B. BONDAREV, A. DURKIN, S. VINOGRADOV, MRTI; J.-M. LAGNIEL, R. N
FERDINAND, CEA/DSM/DAPNIA/SEA
RFQ linac with CW current ~ 100 mA and proton output energy 5-7 MeV can be
used as beginning part of linac for accelerator-driven transmutation
technologies and applications. There are several restrictions using such an
RFQ linac. The radiation purity criterion (minimum of particle lost) is the
main requirement. The RFQ channel must have high transmission (>95%), low
RF field intensity (no more then 1.7 Kilpatrick) and a minimum of particles
lost with energies above 3 MeV. It is also very important to study the
influence of input beam parameter deviation on beam transmission as well as
influence of RFQ channel parameter deviation. The three level code package
LIDOS.RFQ helps to solve all above problems. The optimal choice of main RFQ
channel parameters can be made using the first level codes. The second level
codes are used for correct RF fields calculations taking into account the real
vane geometry. Beam simulation in real RF fields is a main task of the third
level codes. It is possible for LIDOS.RFQ to calculate non-symmetrical
perturbations because there are no assumptions about symmetries both in beam
distributions and in RF field distributions. The new algorithms are discussed
as well as some advantages over much used codes.
Classification Category: D04
TU4047
Multi-fiducial Techniques for Tracking Large Phase Space Distributions
in Non-Linear Fields
S.M. LIDIA, LBNL
One of the challenges in tracking intense beams through linacs is to
account for the differences in nonlinear forces experienced by portions of the
beam separated by large regions of phase space. In many situations, the
high-order map generated by a single fiducial trajectory can fail to
adequately capture or describe the beam dynamics of distant particles. I
describe here a technique which overcomes this difficulty by piecing together
lower-order maps induced by multiple fiducial orbits. This atlas of maps can
more accurately track the evolution of a beam with large phase space extent.
I discuss applications of this technique to simulating beam dynamics in
two-beam accelerators.
Classification Category: D04
TU4048
Production of Negative Hydrogen and Deuterium Ions in Microwave-Driven
Ion Sources*
D. SPENCE, K. R. LYKKE**, ANL
We report progress we have made in the production of negative hydrogen and
deuterium atomic ions in magnetically-confined microwave-driven (2.45 GHz) ion
sources. The influence of source surface material, microwave power, source
gas pressure, and magnetic field configuration on the resulting ion current
will be discussed. Results strongly suggest that, at least in our source,
vibrationally excited molecular hydrogen the precursor to atomic negative ion
production, is produced via a surface mechanism demonstrated by Hall et al.
[1] rather than via a gas phase reaction as is generally believed to be the
case in most ion sources.
*Work supported by USDOE via Argonne LDRD funds.
**Present Address: National Institute of Standards and Technology, Washington,
D.C.
[1] R. J. Hall, I. Cadez, M. Landau, F. Pichou, and C. Schermann, Phys. Rev.
Lett. 60, 337 (1988).
Classification Category: T01
TU4049
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4050
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4051 (oral
poster TU3008)
Doppler-Shift Proton Fraction Measurement on a DC
Proton Injector*
J. H. KAMPERSCHROER, General Atomics; J. D. SHERMAN, T. J. ZAUGG,
LANL; A.
H. ARVIN, A. S. BOLT, SRS
A spectrometer/Optical Multi-channel Analyzer has been used to measure the
proton fraction of a dc proton injector. This technique was pioneered by LBNL
and was subsequently adopted by the international fusion community as the
standard for determining the extracted ion fractions on neutral beam
injectors. Balmer-alpha emission from excited neutral atoms, created in
charge-changing collisions of beams ions with background gas, is observed at
an angle relative to the beam axis. The resulting Doppler-shifts allow the
light emanating from the three extracted ion species to be distinguished from
one another. While the proton emission rate is orders of magnitude lower on
the Low Energy Demonstration Accelerator injector (beam current of tens of mA)
than on fusion neutral beams (tens of A), S/N ratios of 200:1 on the proton
peak and 20:1 on the molecular ion peaks have been obtained by operating with
30-50 micron slits and integrating the light for 16 s. Preliminary analysis
indicates a proton fraction of ~90%, a value in good agreement with results
obtained by magnetically sweeping the ion beam, collimated by a slit, across a
Faraday cup.
*Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T01
TU4052
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4053
Beam Simulations for the H- Injector Upgrade
at
LANSCE*
R. R. STEVENS, JR., W. INGALLS, O. SANDER, B. PRICHARD, JR., J.
SHERMAN,
LANL
An upgrade program is being carried out to increase the beam current from
our present H- injector to provide 200 microamperes current in the
proton
storage ring at LANSCE. In order to meet this objective, the injector must
provide at least 30% more current than presently available [1]. More optimal
operation of the ring, however, requires a factor of two higher peak current
from the injector to reduce circulating losses in the ring. At this higher
current, reduced beam emittance is needed to limit beam losses in the linac.
Beam simulations have been carried out to model the operation of the existing
injector and to determine what changes are needed to obtain higher beam
currents. A collaboration with the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory is now in
progress to modify the present ion source to produce 40 mA of H-
beam with
reduced beam emittance. Appropriate changes will be made in our 80 kV
accelerating column and preinjector beam line in order to accelerate and
transport this higher current beam with acceptable beam size and emittance
growth. Experimental results for the initial phase of this program have been
obtained on our ion source test stand, and these results will be compared with
predictions of the simulations.
* Work supported by the U.S. DOE, Defense Programs.
[1] High Brightness H- Ion Source for LANSCE, Technical Reference
Document for
the SPSS Accelerator Enhancement Project, Internal LANL report, 1997.
Classification Category: T01
TU4054
Ion Source Development for LANSCE Upgrade *
M. WILLIAMS, R. GOUGH, R. KELLER, K. LEUNG, D. MEYER**, A. WENGROW,
LBNL;
O. SANDER, W. INGALLS, B. PRICHARD, R. STEVENS, LANL
The upgrade of the Los Alamos Neutron Science Center (LANSCE) Facility will
require high intensity H- beams. Lawrence Berkeley National
Laboratory(LBNL)
has been contracted by Los Alamos to develop an H- ion generator
that can meet the LANSCE upgrade requirements. Specifically, the output
current of the new H- ion source will be increased from 16 to 40 mA
and maintain approximately the same emittance. In order to meet these
requirements, LBNL has selected the surface-conversion multicusp ion source.
The H- output current of the present LANSCE surface-conversion
source saturates at ~ 20 mA as higher discharge power is applied. Previous
experimental studies at LBNL demonstrated that if the source is operated with
a magnetic filter, the H- output current increases linearly with
the discharge power. During the past year, we have investigated several source
and filter configurations. By placing the converter parallel to the source
axis, we are able to installed six tungsten filaments for the discharge. These
filaments are located inside the cusp magnetic fields of the side wall magnets
which provide the filtering effect. With this new arrangement, the
H- output current was improved from 20 to over 40 mA at the
prescribed 12% duty factor (1 msec pulses at 120 Hz).
*This work was supported by Los Alamos National Laboratory and the U.S.
Department of Energy under Contract No. AC03-76SF00098.
** Permanent address: Kernfysisch Versneller Instituut, The
Netherlands.
Classification Category: T01
TU4055
High Power Test Results of the First SRRC/ANL High Current L-band RF
Gun*
C.H. HO, S.Y. HO, G.Y. HSIUNG, J.Y. HWANG, T.T. YANG, SRRC; M.
CONDE,
W.
GAI, R. KONECNY, J. POWER, P. SCHOESSOW, ANL
There is a joint effort between the SRRC (Synchrotron Radiation Research
Center, Taiwan) and the ANL (Argonne National Laboratory, USA) for developing
a high current L-band rf photocathode gun. We have constructed an L-band (1.3
GHz) , single cell rf photocathode and conducted low power rf test at SRRC.
High power rf conditioning of the cavity will be conducted at ANL. In the high
power test stage, a pair of solenoids will also be used. In this paper, we
report on the construction and high power test results, especially on the dark
current beam loading and rf breakdown at the high axial fields (> 90 MV/m)
.
*Work supported in part by the National Science Council of Taiwan, R.O.C.
under grant No. NSC87-2613-M-213-012.
Classification Category: T01
TU4056
Extraction and Low Energy Transport of Negative Ions *
A. LAKATOS, J. POZIMSKI, A. JAKOB, H. KLEIM, IAP-Univ. of
Frankfurt
High perveance negative ion beams with low emittance are necessary for
several next generation particle accelerators (e.g. neutrons spallation
sources). The production, extraction and transport of these beams have
intrinsic difficulties different from positive ion beams. Therefore intensive
research is necessary to fulfil the project requirements. The low energy
transport from the plasma generator to the entrance of the first accelerator
is limitting the current and the quality of the beam. A cesium free
H- volume source based on the high current source for ESS was
constructed and integrated into an LEBT section to investigate the influence
of beam extraction, electron dumping and space charge compensation on beam
current and emittance. The influence of various parameters like residual gas
pressure, external magnetic and electric fields on beam propagation, space
charge compensation and hence on transmission and emittance growth was
studied. Results of the theoretical and experimental work are presented.
* Work supported by BMFT under contract no. 06 OF 841.
Classification Category: T01
TU4057
Stable Ampere Level Emission of Energetic Electrons
by Electrically Excited Ferrelectric Ceramics
I. BOSCOLO, A. SCURATI, University and INFN-Milano
Stable emission of energetic electrons from ferroelectric ceramic of PLZT
type, i.e. lead zirconate titanate lanthanum doped, in form of thin disks have
been obtained with a proper design of the front electrode. The current is
about 1 A square centimeter and the energy is a couple of keV. High density,
more than 50 A square centimeter, is obtained in the plasma assisted
configuration. The electron expulsion from the surface is due to the
spontaneous polarization switching induced by a high voltage pulse applied to
proper metallic electrodes deposited as thin film on the two surfaces of the
disk. In passing from the usual front electrode having the structure of an
interconnected grating, to an electrode being a pattern of disconnected
patches contained within a ring, the electron emission passes from erratic
with samples and decaying with the number of shots to stable in both cases.
This change in the behavior is explained by the fact that the sandwich of the
continuous electrode and the grating constrains the domain switching and the
relevant charge carriers motion within the part of material covered by metal,
whilst a quasi-free surface allows the domain switching all over the whole
area with the consequent flux of electrons in and out of the sample surface.
In the plasma assisted emission, the front electrode must be the normal
grating because the plasma in this electrode configuration is homogeneous.
Classification Category: T01
TU4058
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4059
Time-Resolved Imaging for the APS Linac Beams*
A. H. LUMPKIN, W. J. BERG, B. YANG, M. WHITE, ANL
The particle-beam imaging diagnostics for the Advanced Photon Source (APS)
injector linac have been enhanced by the installation of optical transition
radiation (OTR) screens and the use of Cs-doped YAG crystals as beam profile
monitors. Both converters have improved spatial resolution and time responses
compared to the standard Chromox (A1203:Cr) screens used
elsewhere in the linac. For the linac macropulse of 30-ns duration composed of
86 micropulses at S-band frequency intervals, only the OTR mechanism is prompt
enough to separate individual micropulses. The OTR also allows synchroscan
streak camera measurements of the micropulse averaged bunch length. Tests have
been performed at 400 to 600 MeV using the gated DC thermionic gun source.
Beam sizes less than 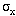 = 60 µ
have been observed with micropulse bunch length of
= 60 µ
have been observed with micropulse bunch length of 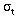 = 2-3 ps
using OTR. Images of accelerated beam from the lower-emittance rf thermionic
gun will be reported as available.
= 2-3 ps
using OTR. Images of accelerated beam from the lower-emittance rf thermionic
gun will be reported as available.
* Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy
Sciences, under Contract No. W-31-109-ENG-38.
Classification Category: T02
TU4060
LEDA & APT Beam Position Measurement System:
Design and Initial Tests*
J. D. GILPATRICK, J. POWER, R. B. SHURTER, M. STETTLER, LANL; J.
O'HARA,
AlliedSignal FM&T/NM
Beam profile measurements are being designed and fabricated for the Low
Energy Demonstration Accelerator (LEDA), a 20-MeV, 100-mA-cw
proton-accelerator, presently under construction at Los Alamos National
Laboratory (LANL). These measurements will provide beam position information
for a steering method which centers the beam within the beam pipe for
Accelerator Production of Tritium (APT) and LEDA. The beam steering method
uses two BPMs and two translatable quadrupole magnets in three successive
focusing-quadrupole magnets every five FODO lattice periods. What makes these
beam position measurements unique is how they will attain their required
accuracy performance and how this accuracy is verified. The position
measurement systems consists of micro-stripline beam position monitors (BPMs)
and rf coaxial cables, log-ratio processors, on-line error correction
sub-systems, and associated algorithms and computer software. This paper will
discuss the mapping of the BPM probes responses, the algorithm used to
calculate their low beam-energy performance, the log ratio processors and its
on-line error-correction, and initial results from bench tests of an
integrated position-measurement system.
* Work suported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T02
TU4061
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4062
Laser Diagnostic for High Current H Beams
R. E. SHAFER, LANL
In the last 5 years, significant technology advances have been made in the
performance, size, and cost of solid-state diode-pumped lasers. These
developments enable the use of compact Q-switched Nd:YAG lasers as a beam
diagnostic for high current H beams. Because the binding energy of the last
electron is only 0.75 eV, and the maximum detachment cross section is 4 E-17
cm2 at 1.5 eV, A 50 mJ/pulse Q-switched Nd:YAG laser can neutralize
a significant fraction of the beam in a single 10-ns wide pulse. The neutral
beam maintains nearly identical parameters as the parent H beam, including
size, divergence, energy, energy spread, and phase spread. A dipole magnet can
separate the neutral beam from the H beam to allow diagnostics on the neutral
beam without intercepting the high-current H beam. Such a laser system can
also be used to extract low current proton beams for cancer therapy treatment,
or induce fluorescence in partially stripped heavy ion beams. Possible
beamline diagnostic systems will be reviewed, and the neutral beam yields will
be calculated for several examples.
Classification Category: T02
TU4063
Horizontal Emittance Measurement in ATF Extraction Line
T. OKUGI, T. HIROSE, Tokyo Metropolitan University; H. HAYANO, K.
KUBO, N.
TERUNUMA, J. URAKAWA, KEK; S. KASHIWAGI, Graduate Univ. for Advanced
Studies
The beam operation of the damping ring in the KEK accelerator test facility
(ATF) has been started since January 1997 for the development of the
technologies to achieve lower emittances, which are required in the future
linear colliders. (The designed emittance in this damping ring is 1.4nm
horizontally and 14pm vertically.) There is a beam extraction line in ATF for
the beam diagnosis of the beam which reduced the emittance in the damping
ring, and the operation of the extraction line has been started since Novenber
1997. However, the position stability at the extraction line doesn't have good
performance for the some reasons of longitudinal and transverse beam
oscillations in the damping ring and the stability of extraction kickers and
so on, the amount of the position fluctuation is 50 to 200micro-m and it
affects the beam size measurement at the ATF extraction line. Therefore, we
established the jitter subtracted beam size measurement for evaluation of the
horizontal beam emittance. In this presentation, the performance of jitter
subtraction and the resulted horizontal emittance in the damping ring will be
presented.
Classification Category: T02
TU4064
Requirements for RF Control of the Vector Sum for Superconducting Proton
Linacs
M. HÜNING, T. SCHILCHER, S.N. SIMROCK, DESY
Superconducting accelerator technology has demonstrated its superior
performance in large scale machines such as CEBA at TJNAF and is increasingly
used for new accelerator designs. Until now this technology has found its main
application in electron accelerators. However nowadays proton accelerator
designs for the European Spallation Source (ESS) and the Accelerator Driven
Transmutation Technology (ADTT) also study the feasibility of superconducting
linacs. In contrast to the highly relativistic electron beams the proton beam
exhibits an increased susceptibility to voltage fluctuations in the
acceleration system induced by microphonics and dynamic Lorentz force
detuning. Although low beam loss is an important criterion for linac design,
studies of the longitudinal dynamics appear to be a good indicator for beam
stability in presence of fluctuations of the accelerating field. Control of
the vector sum of multiple cavities driven by one klystron is desirable for
cost reasons but does not allow for control of individual cavity fields. In
this paper we study the performance of such a system.
Classification Category: T03
TU4065
Time Delay Compensation for the Digital RF Control at the TESLA Test
Facility
H. IMSIEKE, A. KHOLODNYI, T. SCHILCHER, S.N. SIMROCK, DESY
Time delays or dead times between inputs and outputs are an inherent
characteristic of digital feedback systems. The time delay limits the maximum
allowable gain required for system stability. Modern control theory provides a
scheme called Smith predictor which has the potential to improve control
performance significantly. The method is based on model internal control which
works well if the dynamics of the plant are slow compared to the time delay.
In this paper we analyze the performance improvement that can be achieved in
the TTF rf control system where the time delay is dominated by computational
delay. In this system the time delay of 5 microseconds and sampling period of
1 microsecond are short compared to the cavity time constant of 700
microseconds. Attention is paid to both theoretical and practical aspects.
Also investigated is the use of a Smith predictor implementation in hardware
to be used for low Q cavities such as the TTF RF gun cavity.
Classification Category: T03
TU4066
RF Control Studies for Moderate Beamline Coupling Between SRF
Cavities*
L. DOOLITTLE, D.X. WANG, TJNAF
When an SRF accelerator is designed, there is motivation to move the
cavities close together on the beamline. Assuming the beamline apertures are
not shrunk as well, this compaction (which will increase the overall
accelerating gradient and/or lower the dynamic cryogenic heatload) increases
the inter-cavity coupling. Within certain limits, the control system can
compensate for this coupling by retuning each of the cavities. This paper
describes constraints on the RF system, tuners, couplers, and control systems
that are required to provide stable operation of cavities in the presence of
intercavity coupling that exceeds the loaded bandwidth of an individual
cavity.
* Work supported by the U.S. DOE Contract # DE-AC05-84ER40150.
Classification Category: T03
TU4067
The RF System for the CEBAF Polarized Photoinjector*
M. CROFFORD, C. HOVATER, G. LAHTI, TJNAF
The CEBAF electron accelerator has recently begun delivering spin-polarized
electrons for nuclear experiments. Spin-polarized electrons are emitted from a
GaAs photocathode that is illuminated with pulsed laser light from a diode
laser synchronized to the 3rd subharmonic (499 MHz) of the accelerating cavity
frequency (1497 MHz). Up to three experimental halls (A, B and C) are served
by the photoinjector each with their own beam requirements. To accomplish
this, three independent diode lasers are synchronized and combined to
illuminate the GaAs photocathode emitting a 1497 MHz pulse train of electrons.
In addition a RF bunching cavity approximately 2 meters down stream from the
photocathode is used to compensate for space charge effects at the higher beam
currents. The RF system that controls these elements is a modified VME based
system. Custom RF VME modules control phase and amplitude for each laser diode
and the bunching cavity. Power requirements were satisfied with commercial RF
amplifiers, 5 watts for the diode lasers and 10 watts for the bunching cavity.
Phase and amplitude drifts are corrected by simple software algorithms in the
EPICS Input/output computer on the VME crate. The RF system is compact, simple
and allows for easy hardware or software modifications.
* Work supported by the U.S. DOE Contract # DE-AC05-84ER40150.
Classification Category: T03
TU4068
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4069
Waveguide Harmonic Dampers for Klystron Amplifiers *
Y. KANG, A. NASSIRI, ANL
Waveguide harmonic dampers are tested for removing the harmonic frequency
power from the klystron amplifiers of the APS linac. A straight coaxial probe
antenna with a matched load is used in a damper. A linear array of such
dampers is used in the narrow wall of the WR284 waveguide for damping klystron
harmonics while decoupling the dominant TE01 mode to the dampers. The klystron
harmonics may exist in the waveguide as waveguide higher-order modes above
cutoff. Computer simulations are made to optimize the waveguide harmonic
damping characteristics of the harmonic dampers. Other waveguide-type harmonic
dampers are also discussed.
* Work supported by U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy
Sciences under Contract No. W-31-109-ENG-38.
Classification Category: T04
TU4070
Development of a 114.24 MHz Sub-Harmonic Buncher Cavity for the KEKB
Injector Linac
S. YAMAGUCHI, S. OHSAWA, M. IKEDA, A. ENOMOTO, KEK; Y. IGARASHI,
Mitsubishi
Heavy Industries, Ltd., Nagoya Aerospace Systems
A 114.24 MHz sub-harmonic buncher cavity was newly developed to improve the
bunch purity of the KEKB injector linac. The cavity was designed so that it
has high shunt impedance (1.7 times as large as that of the existing cavity)
and low maximum surface field at acceleration gap (less than 10 MV/m for input
power of 10 kW) under the condition that it can be installed in the existing
coils. The cold tests show the unloaded Q-value of 7000 and shunt impedance of
1.2 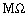 , which satisfy the designed values. To reduce the
probability of rf
breakdown, inner wall of the cavity was electric-polished and vacuum pump-out
was put at the end wall of the cavity. Copper was selected as the structure's
material (it was copper-plated stainless steel for the existing cavity) to
improve the water cooling capability and reduce the frequency change due to
the gap-distance change which comes from input power's up and down. Results of
high-power tests and beam acceleration tests will be described.
, which satisfy the designed values. To reduce the
probability of rf
breakdown, inner wall of the cavity was electric-polished and vacuum pump-out
was put at the end wall of the cavity. Copper was selected as the structure's
material (it was copper-plated stainless steel for the existing cavity) to
improve the water cooling capability and reduce the frequency change due to
the gap-distance change which comes from input power's up and down. Results of
high-power tests and beam acceleration tests will be described.
Classification Category: T04
TU4071 (oral
poster TU3009)
Design, Construction and Operational Results of the
IGBT Controlled Solid State Modulator High Voltage Power Supply used in the High
Power RF systems of the Low Energy Demonstration Accelerator of the Accelerator
Production of Tritium (APT) Project*
J. T. BRADLEY III, D. REES, R. S. PRZEKLASA, LANL; M. C. SCOTT,
Continental
Electronics Corp.
The 1700 MeV, 100 mA Accelerator Production of Tritium (APT) Proton Linac
will require 244 1 MW, continuous wave RF systems. 1 MW continuous wave
klystrons are used as the RF source and each klystron requires 95 kV, 17 A of
beam voltage and current. The cost of the DC power supplies is the single
largest percentage of the total RF system cost. Power supply reliability is
crucial to overall RF system availability and AC to DC conversion efficiency
affects the operating cost. The Low Energy Demonstration Accelerator (LEDA)
being constructed at Los Alamos National Laboratory will serve as the
prototype and test bed for APT. The design of the RF systems used in LEDA is
driven by the need to field test systems with high efficiency and extremely
high reliability before APT is built. We present a detailed description and
test results of one type of advanced high voltage power supply system using
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) that has been used with the LEDA
High Power RF systems. We also present some of the distinctive features
offered by this power supply topology, including crowbarless tube protection
and modular construction which allows graceful degradation of power supply
operation.
* Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T04
TU4072
Design, Operation, and Test Results of 350 MHz LEDA
RF System*
D. REES, J. BRADLEY, K. CUMMINGS, T. HARDEK, W. ROYBAL, LANL
The Low Energy Demonstration Accelerator (LEDA) being constructed at Los
Alamos National Laboratory will serve as the prototype for the low energy
section of Acceleration Production of Tritium (APT) accelerator. The APT
accelerator requires over 244 RF systems each with a continuous wave output
power of 1 MW. The reliability and availability of these RF systems is
critical to the successful operation of APT plant and prototypes of these
systems are being developed and demonstrated on LEDA. The first completed
LEDA RF systems are three, 1.2 MW, 350 MHz, continuous wave, klystrons driving
a radio frequency quadrapole (RFQ). This paper presents the design and test
results for these RF systems including the klystrons, cathode power supply,
circulators, RF vacuum windows, and RF components. The three RF systems
driving the RFQ use the accelerating structure as a power combiner and this
places some unique requirements on the RF systems. These requirements and
corresponding operational implications will be discussed.
*Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T04
TU4073
The RF Power System for the SNS Linac*
P. J. TALLERICO, W. A. REASS, LANL
The initial goal of the SNS project is to produce a 1 MW average, short
pulsed beam of protons onto a neutron-producing target. The objective of the
SNS RF system is to generate 117 MW peak of pulsed 805 MHz microwave power
with an accelerated beam pulse length of 1.04 ms at a 60 Hz repetition rate.
The power system is upgradeable in either peak power or pulse length to
deliver 2 MW average power to the neutron target. The RF system also requires
about 3 MW peak of RF power at 402.5 MHz, which is not discussed here. The
challenge is to produce an RF system near minimum cost, that is very reliable,
and economical to operate. The combination of long pulses, the ability to
double the pulse length in the future, and the repetition rate makes
conventional solutions, such as the pulse transformer and transmission line
very expensive. A 2.5 MW, modulating-anode klystron is the baseline RF
amplifier. We discuss four power systems as candidates for the design. The
baseline is a floating-deck modulating anode system. Next is the fast power
supply, switching with a rise time below 0.1 ms. This can eliminate the
modulator, and drastically reduce energy storage requirements. Next is to use
a pulse transformer with an IGBT switch and a bouncer circuit, as in the
TESLA modulator. Next is to use a series high voltage IGBT switch, without a
pulse transformer. We discuss the advantages and problems of these four types
of power systems, and emphasize the first two.
* Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T04
TU4074
High Power RF Component Testing For NLC
A.E. VLIEKS, W.R. FOWKES, R.J. LOEWEN, S.G. TANTAWI, SLAC
In the Next Linear Collider (NLC), the high power rf components must be
capable of handling peak rf power levels in excess of 600 MW. In the current
view of NLC, even the rectangular waveguide components must transmit at least
300 MW rf power. At this power level, peak rf fields can greatly exceed 100
MV/m. We present recent results of high power tests performed at the
Accelerator Structure Test Area (ASTA) at SLAC. These tests were designed to
investigate the RF breakdown limits of several new components potentially
useful for NLC. In particular we have tested a new type TE01-TE10 circular to
rectangular mode converter, a modified (internal fin) Magic Tee hybrid and an
upgraded flower petal mode converter. We will also present an alternative 3 dB
Hybrid design [1] having improved peak power handling capability.
[1] S. Tantawi, "Boundary Contour Mode Matching Design of an Overmoded
Planar Hybrid," to be published.
Classification Category: T04
TU4075
Linear Inductive Voltage Adders (IVA) for Advanced Hydrodynamic
Radiography*
M. G. MAZARAKIS, J. D. BOYES, D. L. JOHNSON, J. S. LASH, J. E.
MAENCHEN, P.
R. MENGE, C. L. OLSON, S. E. ROSENTHAL, D. C. ROVANG, SNL; B. V. OLIVER, D. R.
WELCH, Mission Research Corp.; V. L. BAILEY, I. D. SMITH, Pulse Sciences
Inc.
The electron beam which drifts through the multiple cavities of
conventional induction linacs (LIA) is replaced in an IVA by a cylindrical
metal conductor which extends along the entire length of the device and
effectuates the addition of the accelerator cavity voltages. In our approach
to radiography, the linear inductive voltage adder drives a magnetically
immersed electron diode with a millimeter diameter cathode electrode and a
planar anode/bremmstrahlung converter. Both anode and cathode electrodes are
immersed in a strong (15-50 T) solenoidal magnetic field. The electron beam
cross section is the same size as the cathode needle and generates a similar
size, very intense x-ray beam when it strikes the anode converter. An IVA
driven diode can produce electron beams of equal size and energy as a LIA but
with much higher currents (40-50 kA versus 4-5 kA), simpler hardware and thus
lower cost. We present here first experimental validations of our technology
utilizing HERMES III and SABRE IVA accelerators. The electron beam voltage and
current were respectively of the order of 10 MV and 40 kA. X-ray doses of up
to 1 kR@1 m and spot sizes as small as 1.7 mm (at 200 R doses) were
measured.
*Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a
Lockheed Martin Company, for the United States Department of Energy under
Contract DE-ACO4-94AL85000.
Classification Category: T04
TU4076
High Performance Pulse Modulater for 80 MW S-Band
Klystron in SPring-8 Linac
T. HORI, H. YOSHIKAWA, T. KOBAYASHI, T. ASAKA, H. SAKAKI, S.
NAGASAWA,
H.
YOKOMIZO, SPring-8
The test-stand of a compact pulse modulator is under construction to carry
out an acceptance test of spare 80 MW S-band klystrons (E3712 TOSHIBA) and to
examine to different type thyratrons (F351 TRITON, CX1937A EEV). This
modulator includes several new technologies such as 40 MHz invertor power
supply for a charging unit, command charging, tunable slugs of PFN coils with
a remote control in order to improve stability of a klystron beam voltage and
to reduce fault rates due to a thyratron prefire as well as to simplify the
maintenance works. Typical specifications of the modulator were 190 MW peak
power, 390kV peak beam voltage, 60pps pulse repitition rates, 2.2 micro-sec
flat top pulse width and less than 0.5% beam voltage stability. This paper
presents the circuit design, specifications and the result of the running
test.
Classification Category: T04
TU4077 (oral
poster TU3010)
The Cold Model of the CDS Structure
L.V. KRAVCHUK, V.V. PARAMONOV, V.A. PUNTUS, INR RAS
The Cut Disk Structure (CDS) was proposed as the compensated accelerating
structure for high energy linacs. Cold rf model was manufactured to examine
the CDS parameters, partially for S-band electron linacs. In agreement with
design parameters coupling coefficient near 22% and high shunt impedance are
obtained. Results of experiments are described.
Classification Category: T05
TU4078
The Bridge Coupling Cavities in the Separated Drift
Tube Linac Structure
L.V. KRAVCHUK, A.S. LEVCHENKO, V.V. PARAMONOV, INR RAS; T. KATO, F.
NAITO,
Y.YAMAZAKI, KEK
The Separated Drift Tube Linac (SDTL) structure was proposed for medium
energy range of proton linacs. The accelerating cavity consists of several
SDTL units with focusing lenses between sections. To drive several SDTL
sections from single rf source, application of both rf power dividers and
coupling bridge cavities seems feasible. Through bridge couplers, the field
distribution, in both amplitude and phase, is automatically stabilised among
connected sections in the first order. Additional rf power dissipation of an
order of several percents is inevitable in the bridge coupler because of its
standing-wave operation. In this paper particularities and limitations for
coupling bridges in the SDTL tanks are considered. Well known cylindrical
bridge cavities may be used. To mantain features of the SDTL structure as the
easy-to-do low-cost one, Rectangular Directly Coupled Bridges (RDCB) look more
preferable. Developed and realised in the main part of INR proton linac, RDCB
operate in TE10n mode and originally have no mode mixing problem. To simplify
manufacturing procedure, RDCB design is based on parts of standard rectangular
waveguide. The philosophy of the SDTL-RDCB tank and results of preliminary
design are presented.
Classification Category: T05
TU4079 (oral
poster TU3011)
324-MHz RF Deflector Design and Test
S. FU*, T. KATO, F. NAITO, K.YOSHINO, KEK
In the design of JHF linac, the beam needs to be chopped for the injection
into the following rapid-cycling ring. The chopper is decided to locate in
the 3-MeV medium-energy transport line between the RFQ and the DTL. The
324-MHz RF deflector (RFD) is adopted as a fast beam-chopper for its various
merits, such as compactness and high deflecting field, which benefit for an
efficient deflection of the beam within a short beam line. In the application
of an RF Deflector for an intense-beam chopper, the beam loss in transient
time is a major concerned issue. The shunt impedance should be as large as
possible to make the cavity to be powered by the commercially available solid
RF source. The RFD cavity is designed by HFSS code to have a very low loaded-Q
value to about 10 by means of two large coupling loops, and meanwhile to keep
the higher order modes sufficiently far away from the deflecting mode. An
Aluminum cold model cavity was made for the test. In this paper, the design,
simulation and the test results are described in detail.
* on leave from China Institute of Atomic Energy
Classification Category: T05
TU4080
Optimization on Wakefield Damping in C-band Accelerating
Structure
N. AKASAKA, H. MATSUMOTO, T. SHINTAKE, KEK
In the C-band rf-system [1], the choke-mode type cavity is used to extract
the HOM power from the beam. It is essential to accelerate low emittance beams
along the main linac of the e+e- linear collider. To damp the HOM power, we
use ring shaped SiC-ceramics, whose dimensions were carefully determined to
optimize the damping performance. This paper describes details of the
optimizing process, which utilizes the time-domain computer simulation of the
transverse wake field. A 1.8 m long structure is under fabrication and it will
be tested with ASSET beam at SLAC in this year.
[1] T. Shintake et al., "C-Band Main Linac RF System for e+e- Linear
Collider of 0.5 to 1.0 TeV C.M. Energy," Linac96, Geneva, August 1996.
Classification Category: T05
TU4081
Design Considerations for Multiple-Beam RFQ Structures
V. KAPIN, M. INOUE, Y. IWASHITA, A. NODA, ICR-Kyoto Univ.
There are applications, which require MeV-range multiple-beams consisting
of a large number of identical highly packed beamlets. The multiple-beam RFQ
(MB-RFQ) arranged as a matrix array of longitudinal rod-electrodes is
appropriate candidate. A configuration of MB-RFQ resonator should ensure
identical quadrupole fields in every accelerating channel. The MB-RFQ
resonators based on TEM transmission lines are studied. The resonators are
designed by a periodical multiplication of a 4-rod unit cell in transverse
direction. To understand fields of resonator the normal mode technique is
applied. The resonator field is expanded into normal modes having simple field
patterns. In general case of resonator with an arbitrary number of rods and
normal modes, analysis becomes difficult. To simplify problem, only normal
modes composed from four normal modes of a 4-rod unit cell are selected.
Similar to normal modes of a 4-rod unit cell (coaxial, quadrupole and two
dipole modes), selected normal modes of multi-rod resonator have clear field
patterns. Novel configurations of MB-RFQ resonators based on these normal
modes are generated. The RF properties of resonators are verified with
computer simulations done with MAFIA code. Features of beam dynamics in MB-RFQ
structures are discussed. The results of beam dynamics simulations are
presented.
Classification Category: T05
TU4082
Proton Beam Studies with a 1.25 MeV, cw Radio Frequency Quadrupole
LINAC*
G.O. BOLME, T.W. HARDEK, L.D. HANSBOROUGH, D.J. HODGKINS, D.R.
KEFFELER,
J.D. SHERMAN, H.V. SMITH, R.R. STEVENS, L.M. YOUNG, T.J. ZAUGG, LANL; P.P.
BALLEYGUIER, CEA/Bruyeres le Chatel; A.H. ARVIN, A.S. BOLT, M.C. RICHARDS,
SRS; J.H. KAMPERSCHROER, General Atomics
A high-current, cw linear accelerator has been proposed as a spallation
neutron source driver for tritium production. Key features of this
accelerator are high current (100 mA), low emittance-growth beam propagation,
cw operation, high efficiency, and minimal maintenance downtime. A 268 MHz,
cw radio frequency quadrupole (RFQ) LINAC section and klystrode based rf
system was obtained from the Chalk River Laboratories [1] and was previously
installed at LANL [2] to support systems development and advanced studies in
support of cw, proton accelerators. A variation of the Low Energy
Demonstration Accelerator (LEDA) proton injector, modified to operate at 50
keV, was mated to the RFQ and was operated to support advance developments for
the Accelerator Production of Tritium (APT) program. High current, proton
beam studies were completed which focused on the details of injector-RFQ
integration, development of beam diagnostics, development of operations
procedures, and personnel and equipment safety systems integration. This
development led to acceleration of up to 100 mA proton beam.
*Work supported by the US Department of Energy.
[1] J.Y. Sheikh et al., "Operation of a High-Power CW Klystrode with the
RFQ1 Facility," Proc. 1993 Particle Accel. Conf., p.
1175.
[2] G.O. Bolme et al., "High-Power RF Operations Studies with the CRITS
RFQ," Proc. 1995 Particle Accel. Conf., p. 923.
Classification Category: T05
TU4083
The Mechanical Design and Fabrication of a Ridge-Loaded Waveguide for an
RFQ
R. VALDIVIEZ, P. ROYBAL, B. CLARK, F. MARTINEZ, D. CASILLAS, G.
GONZALES,
J. TAFOYA, LANL
A Radio Frequency Quadrupole (RFQ) accelerator with an RF power input of 3
MW and an H+ beam output power of 6.7 MeV at 100 mAmps, continuous duty factor
utilizes twelve identical ridge-loaded waveguides to couple the RF power to
the RFQ accelerating cavity. The mechanical design and fabrication of the
ridge-loaded waveguide are the topics of this paper. The waveguide is
rectangular in cross-section, tapers in two planes, and incorporates a center
ridge on the wider dimension with rectangular cavities on either side. The
ridge reduces the internal height of the waveguide from 14.6 centimeters to
0.158 centimeters. The deposited RF power into the waveguide walls increases
with length due to the decreasing cross-sectional dimensions. The deposited
power is accommodated as thermal energy and ranges from 0.053
watts/cm2 at the start of the ridge to 0.85 watts/cm2 at
the RFQ interface. The mechanical analyses that were carried out to predict
the final design characteristics of the ridge-loaded waveguide, as well as the
manufacturing methods and materials used, are also presented.
Classification Category: T05
TU4084
Prototype models for the SNS RFQ*
A. RATTI, J. AYERS, R. GOUGH, J. GREER, M. HOFF, R. KELLER, R.
MCGILL,
J.
STAPLES, R. YOURD, LBNL
Prototype models that simulate components of the RFQ which is part of the
Spallation Neutron Source front end injector are described. The RFQ operates
at 402.5 MHz, a maximum current of 70 mA H- and 6% duty factor. The
copper plated aluminum model is a full size version of one of the four
sections of the RFQ and is used to perform low level r.f. measurements of
frequency, r.f. tuning, field structure and power coupling port studies. This
model is used to benchmark the 3D computer simulation studies and to test
assembly and field measurement procedures. A quarter-wave coaxial resonator is
used to perform full-power tests of high current seals and joints. This model
is also used to test the prototype of the RFQ tuner. The design and
construction of all models are presented, as well as test results.
* This work is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy under contract n.
DEAC0376SF00098.
Classification Category: T05
TU4085
Initial Design of a Charge-State Multiplier System for the RIKEN
RI-Beam Factory Project
O. KAMIGAITO, A. BANDYOPADHYAY*, A. GOTO, Y. YANO, RIKEN
In the RIKEN RI-beam factory project, a Charge-State Multiplier system
(CSM) is planned to be placed between the existing heavy ion linac (RILAC) and
the ring cyclotron (RRC) in order to increase the charge-to-mass ratio (q/A)
of ions without changing the injection radius of the RRC. The CSM consists of
an accelerator, a charge stripper and a decelerator. For the accelerator and
decelerator sections, drift tube linacs of variable-frequency type will be
used, whose rf frequency should be varied from 36 to 76 MHz. The total
accelerating voltage required for the accelerator section is about 26 MV and
that for the decelerator section is about 11 MV. Initial design of the CSM
tanks, based on the IH structure with a movable shorting plate, is described
in this paper.
*On leave from VECC, India.
Classification Category: T05
TU4086
The Present Status of Development on Superconducting Cavities at
SHI
Y. MATSUBARA, M. HIROSE, T. HORI, Laboratory for Quantum Equipment
Technology; H. SAITO, Quantum Equipment Business Center; H. INOUE, M. ONO, E.
KAKO, S. NOGUCHI, K. SAITO, T. SHISHIDO, KEK
We have started development on superconducting cavities with KEK from 1997.
First, we checked out the effect of electropolishing (EP) for a L-band
bulk-niobium single-cell cavity. In the results, we got the relationship
between maximum accelerating field and removed thickness from the cavity
surface, where small amount of EP's were applied repeatedly, and obtained the
high gradient of over 30 MV/m. Next, when fabricating the second, we directly
removed as much the thickness as the optimized depth by the first cavity using
heavy chemicalpolishing and final light EP in sequence. We are now in the
stage of fabricating the third one, 3-cell cavity. In this paper, we will
report on these results and activities at Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Classification Category: T05
TU4087
RF Tests on the Initial 2.8m of the 8m Long ISAC RFQ at
TRIUMF
R. L. POIRIER, A. K. MITRA, TRIUMF
The ISAC RFQ is an 8 meter long, 4-rod split-ring structure operating at 35
MHz in CW mode. The rods are vane-shaped and are supported by 19 rings spaced
40 cm apart. The rings are unique in that the rf surfaces have been de-coupled
from the mechanical support structure to improve dynamic stability. An initial
2.8m section of the accelerator (7 of 19 rings) was installed and aligned in
the 8m, square cross-section, vacuum tank to allow rf and beam tests to be
carried out. The stringent, ± 0.08 mm, quadrature positioning tolerance of the
four rod electrodes was achieved and a relative field variation along the 2.8
meter of the RFQ was measured to be ± 1%, using the standard bead pull method.
The results of the signal level measurements were a frequency of 35.7 MHz, a Q
of 8700 and a resonant shunt impedance of 292 kilohm -meters. Compared to the
3 ring prototype, this represents a 21% increase in Q and a 30% increase in
shunt impedance. The latest results on the full rf power tests on the seven
ring structure will be reported.
Classification Category: T05
TU4088
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4089
Development of a Raster Electronics System for
Expanding the APT Proton Beam*
S. CHAPELLE, E. L. HUBBARD, M. E. SCHULZE, R. E. SHAFER, T. L.
SMITH,
General Atomics
A method of expanding the 1700 MeV, 100 mA proton beam of the APT linear
accelerator onto the tritium production target has been devised using eight
ferrite dipole magnets to deflect the beam in the x and y-plane and paint the
19 cm by 190 cm target uniformly with a rastered pattern. This paper
describes the salient issues of the design of the electronics that are unique
to the expander, including considerations of redundancy, target safety, and
reliability. IGBT-based power modulators drive the raster magnets with
triangular current waveforms which are synchronized using voltage-controlled
crystal oscillators and phase-locked loops. The fault detection circuitry is
also described. Test data are presented for the entire prototype system.
* Work supported by the U.S. DOE under contract DE-AC04-96AL89607.
Classification Category: T07
TU4090
Low to High Energy Beamstops for APT*
D.W. DOLL, T.H. VAN HAGAN, K.M. REDLER, M. FIKANI, G. SPALEK,
General
Atomics; J.D. SCHNEIDER, F.R. SPINOS, W. FUNK, LANL
Beamstops are required for the commissioning and operation of accelerators.
The family of beamstops currently being developed for the DOE-sponsored
Accelerator Production of Tritium (APT) program is addressed. The operational
range encompasses proton energies of 6.7 MeV at the beginning of the RFQ to
1.7 GeV at the target/blanket, and both pulsed and cw operating modes. An
additional beamstop was needed on a companion test facility to validate ion
injector performance. This first of the series of beamstops has been built and
operated; the second is under construction and will be operational by
mid-1998. Particle stopping distance and duty factor drive the size and heat
transfer capacity of these beamstops; the need for low neutron production and
activation potential drives the material selection. At energies above 6.7 Mev,
the preferred beamstop material is graphite with aluminum the choice for
structures and helium the choice for coolant. Boronated water is the preferred
shielding below 70 MeV, but is less suitable at higher energies because of the
creation of Be-7. The evolution of the low-energy demonstration accelerator
(LEDA) to 20 MeV and remaining APT beamstops will be presented with
performance ramifications and updated status of the hardware and testing.
*This work was sponsored by the Department of Energy under Contract No.
DE-AC04-96AL8907.
Classification Category: T07
TU4091
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4092 (oral
poster TU3012)
Design of an Ogive-Shaped Beamstop*
T.H. VAN HAGAN; D.W. DOLL, General Atomics; J.D.
SCHNEIDER, F.R. SPINOS, LANL
This paper addresses the evolution, design, and development of a novel
approach for stopping continuous-wave, non-rastered proton beams. Capturing
the beam in vacuo within a long, axisymmetric surface of revolution has the
advantages of spreading the deposited energy over a large area while
minimizing prompt neutron backstreaming and reducing shield size and mass.
Evolving from a cylinder/cone concept, the ogive shape avoids abrupt changes
in geometry that produce sharp thermal transitions, allowing the beam energy
to be deposited gracefully along its surface. Thermal management at modest
temperature levels is provided with a simple, one-pass countercurrent
forced-convection water passage outside the ogive. Hydrophone boiling sensors
provide overtemperature protection. Photographs and test experience gained to
date on the ogive beamstops for the Chalk River Injector Test Stand (1.2 MeV,
100 kW average power) and the Low Energy Demonstration Accelerator (6.7 MeV,
670 kW average power) proton linacs are included.
*This work is a joint GA/LANL effort sponsored by the U.S.
Department of Energy under contract #DE-AC04-96AL89607.
Classification Category: T07
TU4093
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4094
Low Stored Energy 100 kV Regulator for Ion Sources at
LANSCE*
E. G. JACOBSON, R. L. HAFFNER, W. B. INGALLS, B. J. MEYER, J. S.
STELZER,
LANL
To minimize accelerating-column damage caused by uncontrolled energy
release during arcdown, it is desirable to minimize the available stored
electrical energy. In 1988 Los Alamos Neutron Science Center (LANSCE)
personnel developed an initial design of a low-stored-energy power supply and
planar triode. As priorities for manpower and funding changed over the years,
work on the control circuitry was performed intermittently until construction
of the new Ion Source Test Stand (ISTS). A 120 kV power supply, which has low
output capacitance, and a planar triode have been used to supply the 60 mA,
120 Hz, 12% duty-factor current for the ISTS. The triode's cathode current is
controlled by circuitry operating both at power-supply voltage level and at
ground level via a fiber optic link. Voltage droop is approximately 600 V
during the 1-msec beam pulse. We present the status of the regulator and its
special challenges.
* Work supported by the U. S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: T07
TU4095
Testing of Vacuum Pumps for the APT/LEDA RFQ
K. KISHIYAMA, S. SHEN, LLNL; N. G. WILSON, AMPRO, Inc; D. SCHRAGE,
R.
VALDIVIEZ, LANL
Two vacuum systems were designed and built for the RFQ (Radio Frequency
Quadrupole) cavity which is part of the APT/LEDA (Low Energy Demonstration
Accelerator) linac. The gas load from the proton beam required very high
hydrogen pump speed and capacity for the RFQ cavity vacuum system. The gas
load from the high power RF windows also required very high hydrogen pump
speed for the RF window vacuum system. Cryopumps were chosen for the RFQ
vacuum system and ST185 sintered NEG cartridges were used in the RF window
vacuum system. Hydrogen pump speed and capacity measurements were carried out
for the cryopump and the NEG. This paper will discuss the test procedures and
the preliminary results of the measurements.
Classification Category: T07
TU4096
Medical and Industrial Applications of C-Band Accelerator
Technology
E. TANABE, AET Associates, Inc.; T. SHINTAKE, H. MATSUMOTO, KEK
Electron linear accelerators are commonly used in medical and industrial
applications such as radiation therapy, nondestructive testing and radiation
processing. Most of these accelerators used in various applications are based
on S-band (about 3GHz) microwave technologies. In this paper, C-band microwave
frequencies (5 to 7GHz) are reviewed for medical and industrial applications
in terms of technological limitation, production cost and reliabilities.
Moreover, the C-band technologies of RF components and systems, including RF
sources, solid-state modulators, waveguide components and accelerator
structures will be discussed for new product designs.
Classification Category: U01
TU4097
Assessing the Suitability of a Medical Cyclotron as an Injector for an
Energy Upgrade
J.A. CLARKE, D.M. DYKES, C.W. HORRABIN, H.L. OWEN, M.W. POOLE, S.L.
SMITH,
V.P. SULLER, Daresbury; A. KACPEREK, B. MARSLAND, Clatterbridge
The 60 MeV cyclotron at Clatterbridge operates as the UK centre for proton
therapy, concentrating on treatment of eye tumours; the accelerator is a
Scanditronix model MC60PF fixed energy isochronous cyclotron with a high
current ion source. Although possible energy upgrades have been previously
considered interest has now been reawakened by the activities of the Italian
TERA Foundation, which has proposed a compact high frequency booster linac as
a potential solution to achieve the 200 MeV needed for a broader therapy
programme. The paper reports progress on studies to assess if the Douglas
cyclotron is suitable for a test of such a prototype booster linac. The
results demonstrate that a cyclotron beam pulse of about 25 microseconds can
be achieved by application of amplitude and phase modulation to its RF system.
The most recent measurements of output emittance and energy spread of the
accelerator, in this unusual pulsed mode, are presented and compared with the
normal CW values. Compatibility with the acceptance of the proposed linac is
discussed.
Classification Category: U02
TU4098
A 3 GHz, 200 MeV Proton Linac Booster (LIBO) for
Cancer Treatment
U. AMALDI, A. MILLICH, B. SZELESS, M. VRETENAR, E. J. N. WILSON,
CERN;
J.
E. STOVALL, LANL; K. CRANDALL, Crandall Consult; M. WEISS, Tera Foundation
Proton cyclotrons with output energies of 60 to 70 MeV exist in several
hospitals and laboratories. A high frequency (3 GHz) booster linac (LIBO) is
proposed to upgrade the cyclotron beam to 200 MeV, an energy required to treat
deeply seated cancerous tumors. The LIBO, essentially a side coupled
structure, can produce beams with a variable output energy. This paper
presents the feasibility study of such an accelerator, together with the
1998-1999 milestones, consisting in the machining of a part of the LIBO and
testing it with full RF power on a test stand at CERN.
Classification Category: U02
TU4099
Medical Isotope Production with the Accelerator
Production of Tritium (APT) Facility
M. R. BUCKNER, WSRC; M. CAPPIELLO, E. PITCHER, LANL; H. A.
O'BRIEN,
O'Brien & Associates; K. SPICER, MUSC
A feasibility study of producing radionuclides in the Accelerator
Production of Tritium (APT) Facility has been completed. The APT is a
1700MeV, 100ma accelerator proposed for the Savannah River Site for national
defense purposes. The proton beam produces highly energetic neutrons through
spallation in a tungsten target. Secondary spallation occurs in a lead
blanket which results in an intense neutron source which is moderated for
capture in He-3 to produce tritium. The study concludes that:
- the APT Facility would be ideal for producing diagnostic, therapeutic, and
medical research radionuclides,
- many medical radionuclides could be produced with little or not effect on
tritium production, and
- new and revolutionary techniques could be developed using radionuclides
produced in the APT facility.
When the APT begins operation (~2007), production facilities in the US and
abroad may be obsolete and inadequate to meet the growing demand. The APT
facility could meet that demand. Results of scoping studies for several
promising isotopes will be presented. In addition, the results of a workshop
of nuclear medical leaders in which a consensus endorsement was developed for
the incorporation of these capabilities in APT will be discussed.
Classification Category: U02
TU4100
Operation of High-Power 8.6 and 17.1 GHz Coaxial
Gyroklystrons*
W. LAWSON, B. HOGAN, M. CASTLE, V. L. GRANATSTEIN, M. REISER, X. XU,
Institute for Plasma Research-U. of Maryland
At the University of Maryland, we have designed, constructed, and tested a
number of gyroklystron tubes operating from X-Band to Ka-Band over the past
several years [1]. The purpose of this effort is to examine the suitability of
gyro-amplifiers as drivers for advanced accelerator applications such as the
Next Linear Collider. With a 440 kV, 160-260 A beam, we were able to produce
about 30 MW of peak power in 1 ms pulses near 20 GHz with a second-harmonic
tube. The peak efficiencies were near 30% and the large-signal gains were
about 30 dB. We are currently conducting a series of experiments with coaxial
tubes which are designed to produce peak powers in excess of 100 MW in X- and
Ku-Band, increasing the state-of-the-art by a factor of 3-5. Preliminary
results have indicated peak powers in excess of 75 MW at 8.6 GHz in a three
cavity first-harmonic gyroklystron tube with a gain near 30 dB and an
efficiency near 32%. In this paper we will detail the experimental results of
this tube and discuss designs and preliminary cold and hot test results of a
3-cavity second-harmonic device, which is expected to give comparable results
at 17.14 GHz.
*Work supported by the U. S. Department of Energy.
[1] V. L. Granatstein and W. Lawson, "Gyro-Amplifiers as Candidate RF Drivers
for TeV Linear Colliders," IEEE Trans. on Plasma Science, Vol. 24, pp. 648-665
(1996).
Classification Category: T04
TU4101
Experience at Fermilab with High Quantum Efficiency Photo-Cathodes for RF
Electron Guns
A. FRY, E. HAHN, W. HARTUNG, M. KUCHNIR, FNAL; P. MICHELATO, D.
SERTORE, INFN-Milano
As part of the A0 Photoinjector collaboration at Fermilab, a system was
developed at Milano for coating molybdenum cathodes with a layer of cesium
telluride, a photo-emissive material of high quantum efficiency (QE). The
system incorporates a set of manipulator arms to transfer a cathode from the
preparation chamber into a 1.3 GHz RF electron photo-gun while remaining in an
ultra-high vacuum environment, in order to avoid the deleterious effects of
residual gases on the QE. The electron gun has been operated with a
photo-cathode for several months. The cathode preparation apparatus and
techniques are described. Results of DC QE measurements in the preparation
chamber and pulsed QE measurements in the gun are given. Measurements of the
spatial variation in the QE over the cathode surface and of the time
dependence in the QE are presented. The results of photo-cathode
"rejuvenation" experiments are given.
Classification Category: T01
TU4102
A High Charge Photoinjector for the Pulsed Radiolysis Facility -
ELYSE
M. GAILLARD, Universite de Paris-Sud; J.C. BOURDON, T. GARVEY, J. LE
DUFF, LAL
The Physical Chemistry Department at the Universite de Paris-Sud and the
Laboratoire de l'Accelerateur Lineaire (LAL) will collaborate on a dedicated
radiolysis user facility named ELYSE. The irradiation of user's samples will
be performed using electron beams of energies varying from 4 to 9 MeV,
produced from a laser triggered RF gun. The accelerator group at LAL,
benefitting from the experience gained with their experimental RF gun
(CANDELA), are responsible for the design and construction of the accelerator.
The nominal beam requirements for ELYSE are 1 nC pulses of 5 ps width (FWHM).
However there is a strong scientific interest in obtaining bunch charges of 10
nC for the same pulse width. The need to extract such high charges
neccesitates the use of Cs2Te photocathodes with their high quantum
efficiency. An essential user requirement is to keep the charge of the
integrated dark current during the RF pulse width (3 microseconds) below 1% of
the charge of the main beam. We will present the status of our studies aimed
at the construction of an RF gun and its associated transport optics capable
of achieving these challenging goals.
Classification Category: A01
TU4103
First Performance of the RFD Linac Structure*
D.A. SWENSON, F.W. GUY, K.R. CRANDALL, J.W. LENZ, W.J. STARLING,
Linac Systems
A "Proof-of-Principle" prototype of the Rf-focused Drift tube (RFD) linac
structure is under construction at Linac Systems. This prototype comprises a
25-keV proton ion source, an einzel-lens-based LEBT, a 0.65-m-long RFQ linac
to 0.8 MeV, and a 0.35-m-long RFD linac to 2.5 MeV. These two linac
structures, totaling 1 meter in length, will be resonantly coupled together
and powered by a collection of planar triodes. A basic description of the RFD
linac structure, the beam dynamics within the structure, the tools developed
for its study, and the performance capabilities of the structure will be
presented. Some description of the mechanical design of the components, the
methods used for their fabrication, and the impact of these features on the
cost of RFD-linac-based systems for scientific, medical and industrial
applications will be presented. Performance tests on this prototype are
scheduled to begin in June, 1998. The results of these early performance
tests will be presented.
* Supported by the U.S. National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH).
Classification Category: A02
TU4104
The Performance of the 1.3 GHz Superconducting RF Cavities in the First Module
of the Tesla Test Facility Linac
W.-D. MOELLER, DESY, for the TESLA Collaboration
The design goal on the 1.3 GHz 9-cell superconducting RF cavities for the
Tesla Test Facility (TTF) is a gradient Eacc > 15 MV/m at a quality factor of
Qo > 3e9. The cavities are operated in pulsed mode: 0.8 ms constant gradient
with 10 Hz repetition rate. After the vertical acceptance test and prior to
the assembly in the linac the cavities were tested in a horizontal cryostat
fully equipped with helium vessel, high power input coupler, higher order
modes coupler and tuning system. The first 120 MeV beam has been delivered
successfully by the TTF. We report about the processing of the superconducting
cavity system in the first module and the performance of the cavity system
before, during and after operating the linac.
Classification Category: T05
TU4105
Contribution withdrawn.
TU4106
Simulation of Beam Dynamics Including Space Charge in Proton Linac with
Errors*
D.V. GORELOV**, P.N. OSTROUMOV, INR
LANA computer code (Linear Accelerators Numerical Analysis), has been modified
in order to study the random error effect on beam dynamics in a proton or heavy
ion linac. The standard well known set of different errors of the accelerating
and focusing channel including geometry misalignments in all directions,
magnetic and electric field imperfections and accelerating field instabilities
are included into Monte Carlo simulation of the beam dynamics. Tune-up
procedures for the longitudinal and transverse motion are simulated. Partial as
well as cooperative effects of the errors are analyzed. LANA code includes the
space charge forces of the beam using certain approximation. A comparison of the
errors effect on the beam parameters with and without space charge in the 60 mA
proton linac is presented. As was found the error effect on beam dynamics is a
main contribution on halo formation as well as on beam losses.
* Research was done in frames of the collaboration between INR, Moscow and KEK,
Tsukuba and as part of the agreement between these institutions.
** At present time author has temporary position at NSCL, MSU.
Classification Category: D01
TU4107
Basis for Low Beam Loss in the High-Current APT Linac*
T. P. WANGLER, LANL; K. R. CRANDALL, TECHSOURCE; E. R. GRAY, F. L.
KRAWCZYK, S. KURENNOY, G. P. LAWRENCE, and R. D. RYNE, LANL
We present evidence for the conclusion that the 100-mA, 1700-MeV APT proton
linac design will meet its goals of low beam loss operation. This conclusion
has three main bases: 1) extrapolation from our understanding of the
performance of the 800-MeV LANSCE proton linac at Los Alamos, 2) our theoretical
understanding of the dominant halo-forming mechanism in the APT accelerator from
physics models and multiparticle simulations, including those using high
performance computers, and 3) the conservative approach and key principles
underlying the design of the APT linac, which are aimed at minimizing beam halo
and providing large apertures to reduce beam loss to a very low value.
* Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: D01
TU4108
Design Simulation for Spot Size Stabilization of ITS/DARHT*
T. J. T. KWAN, D. C. MOIR, B. G. DEVOLDER, C. S. SNELL, M. KANG, LANL
DARHT is a flash x-ray machine under construction at Los Alamos. The induction
linac driven electron beam generates x-rays via the bremsstrahlung process in a
converter target. It has been found that the electric field developed between
the electron beam and the target is large enough to draw ions from the target
surface. The ions provide fractional neutralization of the electron beam and
cause it to pinch radially inward. Furthermore, due to the expansion of the ion
column in the upstream direction the location of the pinch point moves in the
same direction resulting in a temporally increasing radiographic spot size
detrimental to the imaging process. The self-biased target concept was proposed
by Kwan and his colleagues in which the electron charge deposited on the target
generates an electric potential which can effectively limit the axial motion of
the ion column and thereby stabilize the growth of the spot size. Detailed
simulations of the beam dynamics have been carried out using MERLIN and MCNP,
and stabilization was achieved at a bias potential of 360kV. A new target
chamber was designed for the Integrated Test Stand (ITS) with beam energy 5.6
MeV and current up to 4 kA. Preliminary results indicate stabilization of the
spot size at the predicted bias potential. Detailed simulation and experimental
results will be presented.
* Work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Classification Category: D01
TU4109
Modeling Beams with Elements in Phase Space*
E. M. NELSON, LANL
Conventional particle codes represent beams as a collection of macroparticles.
An alternative is to represent the beam as a collection of current carrying
elements in phase space. While such a representation has limitations, it may be
less noisy than a macroparticle model, and it may provide insights about the
transport of space charge dominated beams which would otherwise be difficult to
gain from macroparticle simulations.
The phase space element model of a beam is described, and progress toward an
implementation and difficulties with this implementation are discussed. A
simulation of an axisymmetric beam using 1d elements in phase space is
demonstrated.
* Work supported by DOE, contract W-7405-ENG-36.
Classification Category: D01
 to 9
to 9 in quadrupole focusing lattice. This adjustment of
the period was needed to provide sufficient space for the quadrupole focusing
magnets and beam diagnostic equipment. The linac consists of the coupled
cavity drift tube linac [2] up to 100 MeV and coupled cavity linac above 100
MeV.
in quadrupole focusing lattice. This adjustment of
the period was needed to provide sufficient space for the quadrupole focusing
magnets and beam diagnostic equipment. The linac consists of the coupled
cavity drift tube linac [2] up to 100 MeV and coupled cavity linac above 100
MeV. /5 TE111 mode. If these
modes were
adequately damped--which might be possible in the future with minor hardware
changes--then simulations predict that the threshold current would increase by
almost an order of magnitude. The results of these measurements and
simulations, as well as an analytical treatment of the BBU during energy
recovery, are presented.
/5 TE111 mode. If these
modes were
adequately damped--which might be possible in the future with minor hardware
changes--then simulations predict that the threshold current would increase by
almost an order of magnitude. The results of these measurements and
simulations, as well as an analytical treatment of the BBU during energy
recovery, are presented. 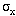 = 60 µ
have been observed with micropulse bunch length of
= 60 µ
have been observed with micropulse bunch length of 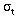 = 2-3 ps
using OTR. Images of accelerated beam from the lower-emittance rf thermionic
gun will be reported as available.
= 2-3 ps
using OTR. Images of accelerated beam from the lower-emittance rf thermionic
gun will be reported as available. , which satisfy the designed values. To reduce the
probability of rf
breakdown, inner wall of the cavity was electric-polished and vacuum pump-out
was put at the end wall of the cavity. Copper was selected as the structure's
material (it was copper-plated stainless steel for the existing cavity) to
improve the water cooling capability and reduce the frequency change due to
the gap-distance change which comes from input power's up and down. Results of
high-power tests and beam acceleration tests will be described.
, which satisfy the designed values. To reduce the
probability of rf
breakdown, inner wall of the cavity was electric-polished and vacuum pump-out
was put at the end wall of the cavity. Copper was selected as the structure's
material (it was copper-plated stainless steel for the existing cavity) to
improve the water cooling capability and reduce the frequency change due to
the gap-distance change which comes from input power's up and down. Results of
high-power tests and beam acceleration tests will be described.